Introduction
TL;DR Your AI system crashed during peak traffic hours yesterday. Customer requests went unanswered for thirty minutes. The pure machine learning approach couldn’t handle edge cases. Your team spent the night firefighting problems that should never have occurred.
This scenario reveals a fundamental flaw in many modern AI deployments. Organizations bet everything on a single approach. They build entirely ML-driven systems or stick with rigid rule-based logic. Neither extreme delivers the reliability businesses actually need.
Hybrid AI workflow architecture solves this critical problem. This approach combines multiple AI techniques strategically. Machine learning handles patterns and predictions. Rules manage compliance and safety checks. Human oversight intervenes when stakes run high.
The result transforms fragile systems into robust operations. You get AI power where it helps most. You maintain control where it matters most. This guide shows you exactly how to build these resilient architectures.
Understanding Hybrid AI Workflow Architecture
Modern AI systems face complexity that single approaches cannot handle alone. Pure machine learning excels at pattern recognition. Traditional programming provides guaranteed behavior. Human judgment brings contextual wisdom.
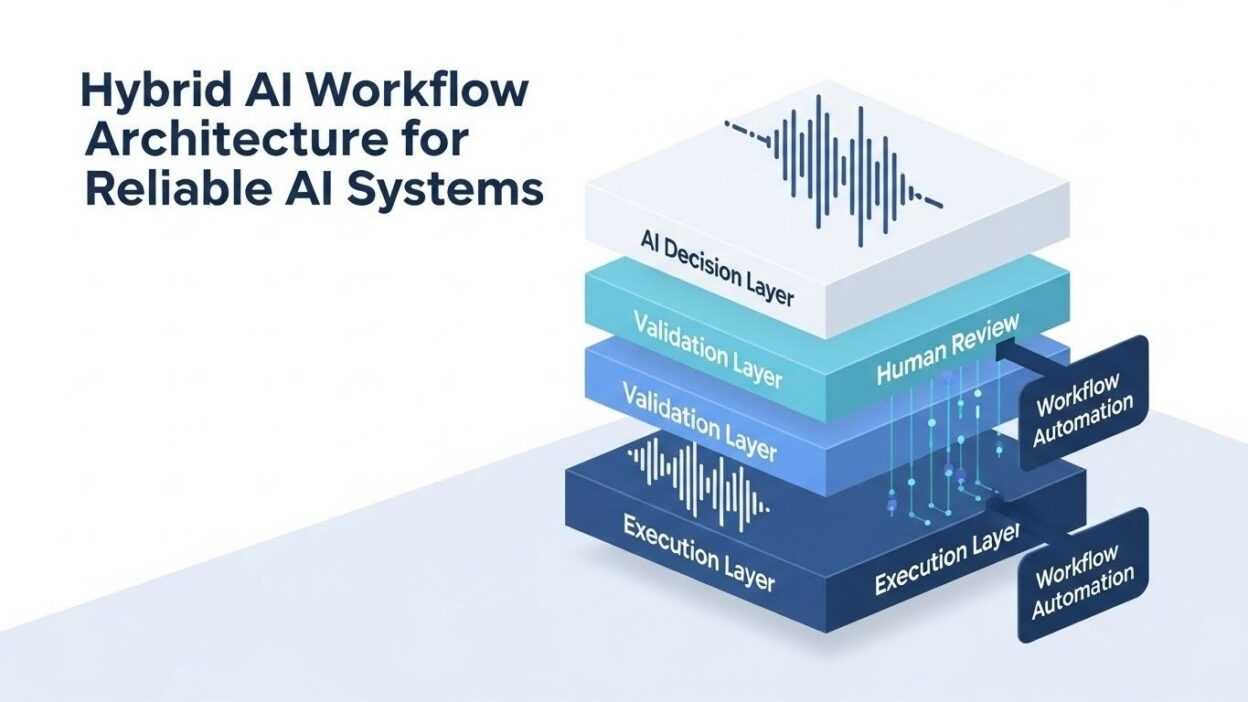
Hybrid AI workflow architecture orchestrates these different capabilities strategically. Each component handles tasks that match its strengths. Machine learning models process unstructured data. Rule-based systems enforce business logic. Human operators make final calls on sensitive decisions.
The architecture differs fundamentally from monolithic AI systems. Multiple processing paths exist within the same workflow. Routing logic determines which component handles each request. Fallback mechanisms activate when primary approaches fail.
Component integration happens at the workflow level rather than the model level. You don’t merge neural networks with decision trees directly. Instead, you connect different systems through well-defined interfaces. This loose coupling enables independent optimization of each part.
The approach acknowledges that no single AI technique solves every problem. Statistical models struggle with rare events. Rule systems become unmaintainable at scale. Humans can’t process millions of decisions daily. Combining approaches covers weaknesses while amplifying strengths.
Understanding this philosophy helps you design better systems. You stop searching for the perfect universal solution. You start building pragmatic architectures that actually work reliably.
The Reliability Problem in Pure AI Systems
Many organizations discovered painful lessons about AI reliability. Systems that worked brilliantly in testing failed spectacularly in production. The gap between lab performance and real-world results shocked technical teams.
Machine learning models suffer from distribution shift. Training data never perfectly matches production data. New patterns emerge constantly. Models trained on historical data struggle with novel situations.
Confidence calibration proves notoriously difficult. Neural networks often express high confidence in wrong answers. Users trust these confident predictions blindly. Catastrophic failures result from misplaced confidence.
Explainability limitations create accountability problems. Black box models make decisions nobody can explain. Regulators demand justifications for automated decisions. Businesses face legal exposure from unexplainable AI choices.
Edge case handling exposes fundamental weaknesses. Rare scenarios appear infrequently in training data. Models never learn to handle these situations properly. Production systems encounter edge cases regularly at scale.
Adversarial vulnerability threatens security and safety. Carefully crafted inputs fool even sophisticated models. Malicious actors exploit these weaknesses deliberately. Financial and reputational damage accumulates quickly.
Degradation over time affects all deployed models. The world changes but models stay static. Performance metrics decline gradually. Organizations discover problems only after significant damage occurs.
Rule-based systems face opposite challenges. They handle known cases perfectly but fail on unexpected inputs. Maintenance becomes impossible as rule counts grow. Brittleness increases with every special case added.
Hybrid AI workflow architecture addresses these reliability problems directly. Multiple techniques provide redundancy and validation. The system maintains functionality even when individual components struggle.
Core Components of Hybrid Architecture
Effective hybrid systems combine specific building blocks strategically. Each component plays a distinct role in the overall workflow.
Machine learning models handle pattern recognition tasks. They process images, text, audio, and sensor data. Statistical learning discovers relationships humans never notice. These models excel at classification and prediction problems.
Rule-based engines encode explicit business logic. They enforce regulatory requirements precisely. Compliance rules execute consistently every time. These systems handle cases where correctness matters more than flexibility.
Human-in-the-loop interfaces enable operator oversight. Experts review high-stakes decisions before execution. Ambiguous cases get escalated automatically. This human judgment layer prevents costly mistakes.
Orchestration layers route requests intelligently. They determine which components handle each input. Confidence thresholds trigger different processing paths. Dynamic routing optimizes for both accuracy and efficiency.
Validation modules verify outputs before execution. Cross-checks between different components catch errors. Sanity tests prevent obviously wrong results. This defensive layer protects against individual component failures.
Feedback systems enable continuous improvement. They collect ground truth labels on predictions. Performance monitoring identifies degrading components. Automated retraining keeps models current.
Data pipelines connect components smoothly. They transform outputs from one component into inputs for another. Format conversions happen transparently. Clean interfaces reduce integration complexity.
Monitoring infrastructure provides visibility into system health. Metrics track each component’s performance independently. Alerts notify teams when problems emerge. This observability enables proactive maintenance.
Designing Routing Logic and Decision Trees
The orchestration layer determines which components handle each request. Smart routing maximizes reliability while maintaining efficiency.
Confidence-based routing sends uncertain cases to more capable components. Machine learning models express confidence scores. Low confidence triggers rule checking or human review. High confidence enables fast automated processing.
Complexity-based routing matches requests to appropriate handlers. Simple cases go through streamlined paths. Complex scenarios activate comprehensive analysis. This tiering prevents over-engineering simple problems.
Risk-based routing escalates high-stakes decisions. Financial thresholds trigger additional validation. Safety-critical choices always involve human oversight. The system balances speed with appropriate caution.
Fallback chains provide graceful degradation. Primary components attempt processing first. Failures trigger secondary approaches automatically. This redundancy maintains service during component outages.
Load-based routing distributes work efficiently. Multiple models handle different request segments. Processing load spreads across available resources. Performance remains consistent under varying demand.
Context-aware routing considers situational factors. Time of day affects routing decisions. User history influences processing paths. Geographic location determines regulatory requirements.
A/B testing routing enables continuous optimization. Different routing strategies run in parallel. Performance metrics guide strategy refinement. This experimentation improves routing logic over time.
Exception handling catches unexpected conditions. Edge cases receive special processing paths. Unusual inputs trigger safety mechanisms. The system fails safely rather than catastrophically.
Implementing Rule-Based Safety Guardrails
Rules provide deterministic safety checks that machine learning alone cannot guarantee. These guardrails prevent dangerous mistakes regardless of model behavior.
Input validation enforces data quality requirements. Type checking catches malformed requests. Range validation prevents absurd values. These pre-checks stop problems before processing begins.
Business logic enforcement maintains domain constraints. Regulatory compliance rules execute unconditionally. Policy requirements get validated systematically. No ML model can override these hard limits.
Output sanitization prevents harmful results. Financial transactions respect account limits. Dangerous recommendations get filtered automatically. These post-checks protect users from AI mistakes.
Consistency validation ensures logical coherence. Cross-field relationships get verified. Contradictory outputs trigger rejection. This catches nonsensical results before execution.
Temporal validation considers timing constraints. Actions respect business hours and deadlines. Historical consistency gets checked. Time-based rules prevent anachronistic decisions.
Authorization checks enforce access controls. Security policies apply universally. Permission requirements get validated. This prevents unauthorized actions regardless of AI recommendations.
Rate limiting protects system resources. Request frequency gets throttled appropriately. Abuse detection triggers automatically. These mechanisms prevent both accidents and attacks.
Rollback capabilities enable mistake recovery. Dangerous actions require confirmation. Undo mechanisms exist for reversible operations. This safety net reduces consequences of errors.
Audit logging creates accountability trails. Every rule check gets recorded. Decision justifications remain available. This transparency supports compliance and debugging.
Machine Learning Model Selection and Integration
Choosing appropriate ML techniques for each workflow component maximizes overall system performance. Different problems demand different solutions.
Classification models handle categorization tasks. Support vector machines excel at binary decisions. Neural networks manage multi-class problems. Random forests provide good baseline performance.
Regression models predict continuous values. Linear regression handles simple relationships. Gradient boosting captures complex interactions. Deep learning scales to huge datasets.
Clustering algorithms discover natural groupings. K-means provides fast segmentation. Hierarchical methods reveal structure. These unsupervised approaches handle unlabeled data.
Anomaly detection identifies unusual patterns. Isolation forests spot outliers efficiently. Autoencoders learn normal behavior. Statistical tests provide interpretable results.
Natural language processing extracts meaning from text. Transformers dominate modern NLP tasks. Named entity recognition pulls structured data. Sentiment analysis gauges emotional content.
Computer vision processes visual information. Convolutional networks excel at image tasks. Object detection locates items in scenes. Semantic segmentation classifies every pixel.
Recommendation systems suggest relevant items. Collaborative filtering leverages user behavior. Content-based approaches use item features. Hybrid recommenders combine both techniques.
Time series forecasting predicts future values. ARIMA models handle stationary series. LSTMs capture long-term dependencies. Prophet accommodates seasonality easily.
Ensemble methods combine multiple models. Voting aggregates diverse predictions. Stacking learns optimal combination weights. This increases robustness and accuracy.
Human-in-the-Loop Integration Patterns
Human expertise remains irreplaceable for certain decision types. Smart integration patterns leverage human judgment effectively.
Active learning selects informative examples for labeling. Models identify uncertain predictions. Humans label these critical cases. This targeted annotation maximizes learning efficiency.
Confidence-based escalation routes unclear cases to experts. Automated thresholds trigger human review. Experts handle only ambiguous situations. This scales human oversight efficiently.
Collaborative filtering leverages human feedback. Users rate system outputs explicitly. Thumbs up/down signals guide improvements. This creates virtuous improvement cycles.
Expert validation confirms high-stakes decisions. Automated systems make recommendations. Humans approve before execution. This maintains accountability for critical choices.
Anomaly investigation employs human pattern recognition. Systems flag unusual cases automatically. Experts determine whether anomalies matter. This combines scale with contextual understanding.
Correction mechanisms enable mistake recovery. Users can override incorrect outputs. These corrections feed back into training. Systems learn from their errors continuously.
Batch review processes handle lower-priority decisions. Humans review accumulated cases periodically. This balances thoroughness with efficiency. Not everything needs instant attention.
Quality assurance sampling validates automated processing. Random samples get human review. Statistical confidence emerges from samples. This verifies system reliability over time.
Context provision helps humans make better decisions. Systems present relevant information clearly. Decision-supporting data appears alongside cases. This augments rather than replaces human judgment.
Data Pipeline Architecture for Hybrid Systems
Moving data between different processing components requires careful pipeline design. Clean data flow prevents errors and maintains performance.
Ingestion layers normalize incoming data. Different sources provide different formats. Standardization happens at entry points. Downstream components consume consistent data structures.
Transformation stages prepare data for each component. ML models need normalized features. Rule engines require structured attributes. Format conversions happen transparently.
Feature engineering creates useful model inputs. Domain knowledge guides feature creation. Automated feature generation supplements manual engineering. Good features dramatically improve model performance.
Validation checks ensure data quality. Missing values get handled appropriately. Outliers receive special treatment. These checks prevent garbage-in-garbage-out problems.
Caching reduces redundant processing. Frequently accessed data stays in memory. Expensive computations get memoized. This improves response times significantly.
Versioning tracks data evolution. Schema changes get managed explicitly. Backward compatibility prevents breakage. This enables safe system updates.
Monitoring tracks data quality metrics. Distribution shifts get detected automatically. Anomalies trigger investigations. This early warning system prevents silent failures.
Lineage tracking documents data provenance. Origins of every value remain traceable. This supports debugging and compliance. Understanding data flow aids troubleshooting.
Monitoring and Observability Strategies
Hybrid AI workflow architecture requires comprehensive monitoring across all components. Visibility enables proactive problem detection and resolution.
Component-level metrics track individual subsystem performance. Model accuracy gets measured continuously. Rule execution times stay within bounds. Human review latency remains acceptable.
End-to-end metrics measure overall workflow success. Task completion rates indicate system health. User satisfaction scores reflect actual value. These outcome metrics matter most ultimately.
Confidence distribution analysis reveals model calibration. Well-calibrated models show appropriate uncertainty. Overconfidence signals potential problems. This helps set routing thresholds correctly.
Error rate tracking by component identifies weak links. Which subsystem causes most failures? Where do errors originate? This guides improvement priorities.
Latency measurement ensures responsiveness. Each processing stage gets timed. Bottlenecks get identified quickly. Performance optimization focuses on slowest components.
Resource utilization monitoring prevents capacity problems. CPU and memory usage stay reasonable. Scaling triggers activate appropriately. This prevents performance degradation under load.
Drift detection identifies changing data patterns. Model inputs shift over time. Performance degradation correlates with drift. This signals retraining needs proactively.
Alert systems notify teams of problems. Threshold breaches trigger notifications. Anomalies get flagged automatically. Escalation procedures activate for critical issues.
Dashboard visualization presents metrics clearly. Time series graphs show trends. Heat maps reveal patterns. This situational awareness supports decision-making.
Testing Hybrid AI Systems
Validating hybrid architectures requires specialized testing approaches. Each component and their interactions need thorough validation.
Unit testing validates individual components. ML models get tested on held-out data. Rules execute against test cases. Human interfaces undergo usability testing.
Integration testing verifies component interactions. Do outputs from one component feed properly into the next? Do format conversions work correctly? These tests catch interface problems.
End-to-end testing validates complete workflows. Real user scenarios get simulated. Edge cases receive explicit testing. This ensures the whole system works together.
Performance testing measures system capacity. Load testing reveals breaking points. Stress testing pushes beyond normal conditions. This establishes operational limits clearly.
Regression testing prevents quality degradation. Every update runs standard test suites. Known good cases must still pass. This catches unintended consequences early.
A/B testing compares alternative approaches. Different routing strategies run in parallel. Performance metrics guide selection. Data-driven decisions replace opinions.
Shadow testing validates changes safely. New components process real data. Results don’t affect production. This proves reliability before full deployment.
Chaos engineering tests resilience. Components fail deliberately. System response gets observed. This validates fault tolerance mechanisms.
Red team exercises probe security. Adversarial inputs attempt to fool systems. Exploits get discovered proactively. This hardens defenses before attacks occur.
Deployment Patterns and Scaling Strategies
Moving hybrid architectures to production requires careful deployment planning. Different patterns suit different organizational needs.
Blue-green deployment enables zero-downtime updates. New versions run alongside old ones. Traffic switches after validation. Rollback happens instantly if problems emerge.
Canary releases limit blast radius. Small user percentages see changes first. Gradual rollout proceeds with validation. This catches problems before wide impact.
Feature flags enable selective activation. New capabilities toggle on/off dynamically. Different users experience different features. This supports experimentation safely.
Microservices architecture enables independent scaling. Each component deploys separately. Resource allocation matches actual demand. This optimizes infrastructure costs.
Container orchestration manages deployment complexity. Kubernetes handles scaling automatically. Health checks maintain service quality. This operational automation reduces manual work.
Edge deployment reduces latency. Processing happens closer to users. Critical components run locally. This improves responsiveness significantly.
Multi-region deployment ensures availability. Geographic distribution increases reliability. Regional failures don’t cause total outages. This satisfies business continuity requirements.
Load balancing distributes traffic effectively. Multiple instances handle parallel requests. Failed instances get bypassed automatically. This maintains performance under varying loads.
Auto-scaling adjusts capacity dynamically. Metrics trigger scaling actions. Resources match actual demand. This balances performance and cost.
Cost Optimization in Hybrid Architectures
Hybrid systems involve multiple components with different cost structures. Strategic optimization reduces total cost of ownership.
Compute allocation matches component needs. GPU-intensive models get appropriate hardware. Simple rules run on basic instances. This right-sizing prevents waste.
Caching reduces redundant processing. Frequently requested predictions get stored. Expensive computations happen once. This dramatically cuts costs for common queries.
Batch processing groups similar requests. Throughput optimization improves efficiency. Latency-sensitive items get real-time processing. This dual approach balances speed and cost.
Model compression reduces inference costs. Quantization shrinks model sizes. Pruning removes unnecessary parameters. Distillation transfers knowledge to smaller models.
Tiered processing sends simple cases through cheap paths. Complex cases justify expensive analysis. This dynamic routing optimizes cost-performance tradeoffs.
Reserved capacity planning locks in discounts. Predictable workloads buy committed resources. Spot instances handle variable demand. This mixed approach minimizes cloud costs.
Monitoring identifies cost inefficiencies. Which components consume most resources? Where does money get wasted? This visibility guides optimization efforts.
Open-source alternatives reduce licensing fees. Community models provide baseline capabilities. Commercial solutions handle specialized needs. This mixed approach controls costs.
Security Considerations for Hybrid Systems
Multiple components create multiple attack surfaces. Comprehensive security protects hybrid AI workflow architecture effectively.
Input validation prevents injection attacks. Malicious payloads get rejected. Type checking enforces safety. This defensive posture blocks common exploits.
Authentication and authorization secure access. Every component verifies identity. Permission checks happen consistently. This prevents unauthorized usage.
Encryption protects data in transit and at rest. Sensitive information stays encrypted. Keys get managed securely. This prevents data breaches.
Model security prevents adversarial attacks. Input perturbation detection catches attacks. Ensemble defenses increase robustness. This hardens ML components specifically.
Audit logging creates accountability. Every action gets recorded. Security events trigger alerts. This supports forensics and compliance.
Network segmentation isolates components. Compromised parts can’t spread laterally. Firewalls enforce boundaries. This limits breach impact.
Secrets management protects credentials. API keys stay out of code. Rotation happens automatically. This prevents credential theft.
Vulnerability scanning identifies weaknesses. Regular security assessments occur. Patches get applied promptly. This maintains security posture.
Incident response procedures enable rapid recovery. Breach detection triggers protocols. Containment prevents damage spread. This minimizes security incident impact.
Compliance and Governance Framework
Regulated industries face strict requirements for AI systems. Hybrid architectures must satisfy these demands comprehensively.
Explainability mechanisms justify decisions. Rule-based components provide clear logic. ML explanations use interpretable techniques. This transparency satisfies auditor requirements.
Audit trails document every decision. Who approved what and when? Which components contributed? This traceability supports compliance.
Bias monitoring ensures fairness. Demographic analysis reveals disparities. Mitigation strategies address identified biases. This promotes equitable outcomes.
Version control tracks system evolution. Every configuration gets recorded. Changes require approval. This change management prevents unauthorized modifications.
Access controls enforce least privilege. Users see only necessary information. Operators can’t modify production data. This separation protects integrity.
Retention policies manage data lifecycle. Information gets deleted appropriately. Regulatory requirements get satisfied. This reduces long-term liability.
Impact assessments evaluate risks. New features undergo review. Potential harms get identified. This proactive approach prevents problems.
Governance committees oversee AI usage. Cross-functional teams make policy. Regular reviews maintain standards. This organizational oversight ensures responsibility.
Case Studies and Real-World Applications
Organizations across industries deploy hybrid AI workflow architecture successfully. These examples illustrate practical implementations.
Financial services use hybrids for fraud detection. ML models flag suspicious transactions. Rules enforce regulatory checks. Human analysts investigate complex cases. This combination catches fraud while minimizing false positives.
Healthcare systems combine AI and clinical judgment. Models analyze medical images automatically. Rule checks verify protocol compliance. Doctors make final diagnostic decisions. Patients receive both efficiency and expert care.
Manufacturing employs hybrids for quality control. Computer vision inspects products. Statistical tests validate measurements. Operators handle ambiguous defects. Production maintains high quality at scale.
Customer service integrates bots and humans. Chatbots handle routine inquiries. Escalation rules route complex issues. Agents resolve difficult cases. Customers get fast help appropriately.
Supply chain optimization balances algorithms and expertise. Forecasting models predict demand. Constraint solvers optimize logistics. Managers override for special circumstances. Operations run smoothly despite uncertainty.
Content moderation combines automation and review. ML filters obvious violations. Ambiguous content reaches moderators. Appeal processes involve human judgment. Platforms maintain safety at scale.
Autonomous vehicles exemplify safety-critical hybrids. Neural networks perceive environments. Rules enforce traffic laws. Emergency protocols enable human takeover. This layered approach pursues safety rigorously.
Frequently Asked Questions
What exactly makes an AI workflow hybrid?
Hybrid AI workflow architecture combines multiple AI techniques within single systems. Machine learning models handle pattern recognition. Rule-based logic enforces business constraints. Human judgment guides critical decisions. The system routes requests to appropriate components dynamically. This integration creates resilience that single approaches cannot achieve. Each technique handles tasks matching its strengths. The orchestration layer coordinates everything smoothly.
How does hybrid architecture improve reliability compared to pure ML?
Pure machine learning fails on edge cases and adversarial inputs. Hybrid systems add validation layers that catch these failures. Rules provide guaranteed safety checks. Human oversight prevents costly mistakes. Multiple processing paths create redundancy. If one component struggles, others compensate. Validation between components catches errors. This defense-in-depth approach dramatically increases reliability.
What skills do teams need for building hybrid systems?
Teams need diverse expertise spanning multiple disciplines. Machine learning engineers handle model development. Software architects design system integration. Domain experts contribute business logic. DevOps engineers manage deployment infrastructure. Data engineers build pipelines. Project managers coordinate across specialties. No single person masters everything. Cross-functional collaboration proves essential.
How much does implementing hybrid architecture cost?
Costs vary dramatically based on system complexity. Initial development typically costs more than pure ML. Multiple components require more engineering effort. Long-term costs often decrease compared to alternatives. Better reliability reduces incident response expenses. Fewer mistakes mean less damage control. Maintenance gets easier with modular design. ROI typically justifies investment within one year.
Can I add hybrid architecture to existing ML systems?
Absolutely. Most organizations retrofit existing systems gradually. Start by adding validation rules around current models. Introduce human review for high-confidence failures. Build orchestration layers over time. Microservices patterns enable incremental migration. Legacy components continue operating during transition. This evolutionary approach minimizes risk. Complete rewrites rarely make sense.
What performance overhead does hybrid architecture introduce?
Additional components add some latency inevitably. Simple rule checks add milliseconds typically. Human review introduces minutes or hours. Smart routing minimizes overhead for common cases. Caching reduces repeated processing costs. Parallel execution masks some delays. Overall impact depends on implementation quality. Well-designed systems maintain acceptable performance.
How do I decide what stays ML versus rules?
Several factors guide this decision clearly. Use ML for pattern recognition in unstructured data. Use rules for compliance and safety requirements. Let ML handle high-volume repetitive decisions. Reserve rules for critical accuracy requirements. Consider explainability needs carefully. Regulatory constraints often demand rules. Cost-benefit analysis helps for edge cases.
What monitoring tools work best for hybrid systems?
General observability platforms provide foundations. Prometheus tracks metrics across components. Grafana visualizes performance dashboards. Specialized ML monitoring tools track model-specific metrics. Custom instrumentation handles hybrid-specific needs. Logging aggregation systems collect audit trails. APM solutions trace requests across components. Comprehensive monitoring requires multiple tools working together.
How often should hybrid systems get updated?
Update frequency varies by component type. ML models need retraining monthly or quarterly. Rules get updated as regulations change. Human procedures evolve with business needs. Infrastructure patches apply continuously. Version everything independently. Coordinate updates to prevent incompatibilities. Continuous deployment works for some components. Critical changes require careful staging.
What are biggest mistakes in hybrid system design?
Over-engineering simple problems wastes resources. Adding unnecessary complexity hurts reliability. Unclear component boundaries create confusion. Insufficient monitoring leaves teams blind. Neglecting human factors causes workflow failures. Poor error handling breaks gracefully degradation. Ignoring security creates vulnerabilities. Skipping proper testing invites disasters. Most problems come from inadequate planning.
Read More:-Call Quality Scoring with AI vs Manual QA
Conclusion

Hybrid AI workflow architecture represents the mature approach to building reliable AI systems. Pure machine learning provides impressive capabilities but insufficient reliability. Traditional programming offers predictability but limited intelligence. Human judgment brings wisdom but doesn’t scale.
Combining these approaches creates systems greater than their parts. Machine learning handles pattern recognition at scale. Rules enforce safety and compliance unconditionally. Humans provide oversight where stakes justify involvement. Orchestration logic routes requests optimally.
The reliability gains justify implementation complexity. Edge cases get handled gracefully. Adversarial attacks get detected and blocked. Performance degradation triggers appropriate responses. Your systems maintain functionality despite individual component struggles.
Start implementing hybrid architecture incrementally. Add validation rules around existing models first. Introduce human review for high-stakes decisions. Build orchestration capabilities gradually. This evolutionary approach minimizes risk while building capability.
Monitor comprehensive metrics across all components. Track model accuracy, rule execution, and human decisions. End-to-end workflow metrics reveal true performance. Continuous monitoring enables proactive problem detection.
Test thoroughly at every level of abstraction. Unit tests validate individual components. Integration tests verify interactions. End-to-end tests prove complete workflows. This testing discipline prevents embarrassing failures.
Scale thoughtfully as demand grows. Microservices enable independent component scaling. Containerization simplifies deployment complexity. Auto-scaling matches capacity to load. These modern practices support growth efficiently.
Secure every component and interaction. Multiple components create multiple attack surfaces. Defense-in-depth strategies protect comprehensively. Regular security assessments maintain posture. This vigilance prevents breaches and builds trust.
Maintain compliance through systematic governance. Audit trails document every decision. Explainability mechanisms justify automated choices. Bias monitoring ensures fairness. These practices satisfy regulatory requirements.
Learn from early hybrid adopters across industries. Financial services, healthcare, and manufacturing show the way. Their successes prove the approach works. Their mistakes teach valuable lessons.
Your AI systems deserve the reliability hybrid architecture provides. Users depend on consistent performance. Businesses require predictable operations. Hybrid AI workflow architecture delivers both intelligence and dependability. The future of AI belongs to systems that combine approaches thoughtfully.
Take the first step today toward building truly reliable AI systems. Your users will notice the difference. Your business will benefit from the stability. The investment in hybrid architecture pays dividends for years to come.