Introduction
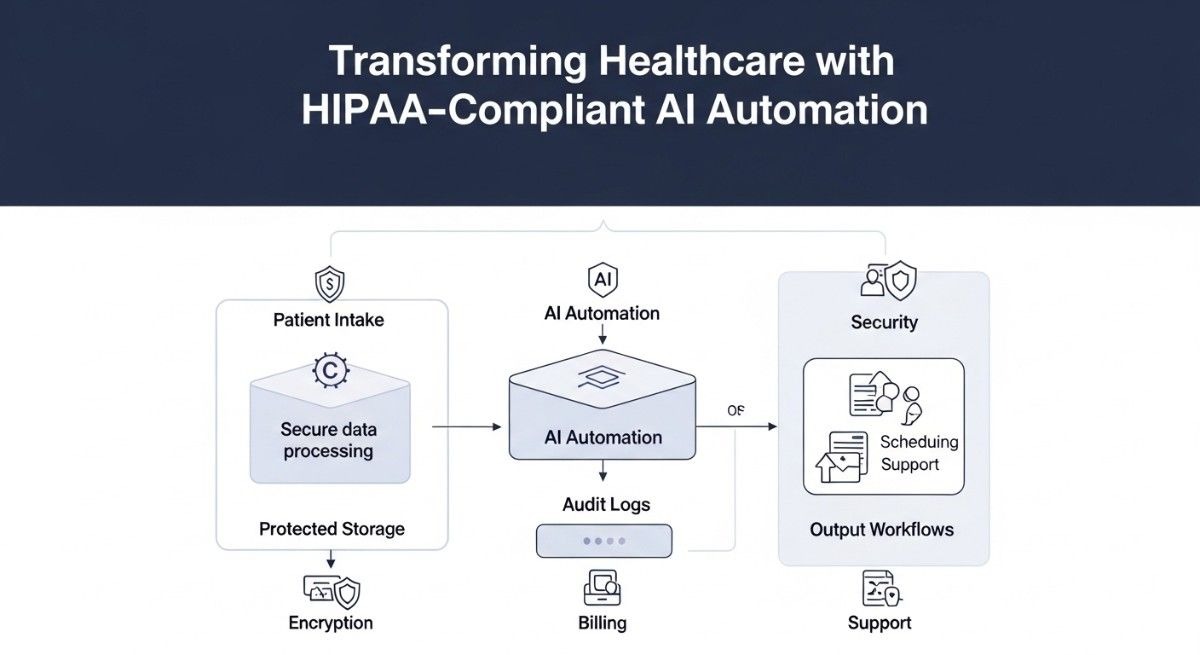
TL;DR Healthcare organizations face mounting pressure to deliver better patient outcomes. Administrative burdens consume valuable time and resources. HIPAA-compliant AI automation offers a transformative solution that balances efficiency with regulatory requirements.
Medical professionals spend hours on documentation, scheduling, and billing tasks. Patient care suffers when administrative work overwhelms clinical staff. Artificial intelligence streamlines these processes while maintaining strict privacy standards.
The healthcare industry generates massive volumes of sensitive data daily. Electronic health records, insurance claims, and diagnostic images require careful handling. Automation technologies must respect patient privacy while delivering operational benefits.
Table of Contents
Understanding HIPAA Compliance in Healthcare AI
The Fundamentals of HIPAA Regulations
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act establishes strict data protection standards. Protected health information includes any data that identifies individual patients. Names, birth dates, social security numbers, and medical record numbers all qualify as PHI.
Healthcare providers must implement safeguards across three domains. Physical security protects facilities and equipment from unauthorized access. Technical controls secure electronic systems and data transmissions. Administrative policies govern employee training and incident response.
Covered entities include hospitals, clinics, insurance companies, and clearinghouses. Business associates who handle PHI on behalf of providers also face compliance obligations. Software vendors, billing services, and cloud storage providers must sign business associate agreements.
Penalties for HIPAA violations range from minor to catastrophic. Civil fines start at $100 per violation and reach $50,000 for willful neglect. Criminal charges can result in imprisonment for intentional privacy breaches.
Patient rights under HIPAA include access to their medical records. Individuals can request corrections to inaccurate information. Breach notifications must occur within 60 days of discovery.
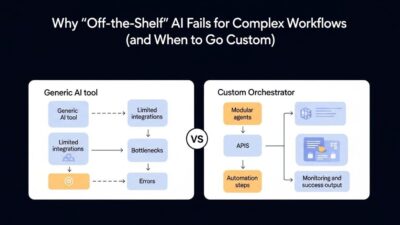
Why Traditional Automation Falls Short
Legacy automation systems lack sophisticated security controls. Simple workflow tools cannot distinguish between sensitive and non-sensitive data. Rule-based systems require constant manual updates to maintain compliance.
Traditional electronic health record systems often create silos. Data trapped in isolated systems prevents comprehensive patient care. Interoperability challenges plague healthcare organizations nationwide.
Robotic process automation handles repetitive tasks effectively. These systems cannot understand context or make intelligent decisions. Complex medical scenarios require human-like reasoning capabilities.
Paper-based processes persist in many healthcare settings. Manual data entry introduces errors and slows operations. Digital transformation becomes essential for modern healthcare delivery.
Compliance requirements change as regulations evolve. Static automation solutions cannot adapt to new rules automatically. HIPAA-compliant AI automation provides the flexibility healthcare organizations need.
The Role of AI in Modern Healthcare
Machine learning algorithms analyze medical images with remarkable accuracy. Radiologists receive decision support for cancer detection and diagnosis. Computer vision identifies abnormalities that human eyes might miss.
Natural language processing extracts insights from clinical notes. Unstructured physician documentation becomes structured, searchable data. Coding and billing processes accelerate through intelligent text analysis.
Predictive analytics identify patients at risk for adverse events. Hospital readmission models help care teams intervene proactively. Population health management improves through data-driven insights.
Virtual health assistants answer patient questions around the clock. Chatbots schedule appointments and provide medication reminders. Patient engagement increases through convenient digital interactions.
Clinical decision support systems recommend treatment protocols. Evidence-based guidelines get integrated into physician workflows. Quality of care improves through real-time knowledge delivery.
Core Components of HIPAA-Compliant AI Systems
Data Encryption and Security Measures
Encryption protects patient data both in transit and at rest. AES-256 encryption meets current healthcare security standards. Cryptographic keys require secure management and regular rotation.
Transport layer security secures data moving between systems. TLS 1.3 provides the strongest protection for network communications. Certificate validation prevents man-in-the-middle attacks.
Database encryption shields stored patient information from unauthorized access. Column-level encryption protects especially sensitive fields. Encryption key management systems prevent single points of failure.
Tokenization replaces sensitive data with non-sensitive substitutes. Payment information and social security numbers become random tokens. Original values remain in secure vaults separate from operational systems.
Secure enclaves provide hardware-based protection for critical operations. Trusted execution environments isolate sensitive computations. Even system administrators cannot access data in these protected zones.
End-to-end encryption ensures only intended recipients access messages. Secure messaging platforms protect physician-patient communications. Email encryption prevents interception during transmission.
Access Controls and Authentication
Role-based access control limits data visibility to authorized personnel. Physicians see different information than billing staff. Minimum necessary standard governs access permissions.
Multi-factor authentication strengthens user verification processes. Passwords alone provide insufficient security for sensitive systems. Biometrics, tokens, and one-time codes add protection layers.
Single sign-on reduces password fatigue while maintaining security. Centralized authentication simplifies access management. HIPAA-compliant AI automation integrates with enterprise identity systems.
Privileged access management monitors administrative activities. Elevated permissions receive extra scrutiny and logging. Just-in-time access grants temporary elevated privileges when needed.
Session management prevents unauthorized access through abandoned workstations. Automatic timeout policies log users out after inactivity. Concurrent session limits prevent credential sharing.
Attribute-based access control enables fine-grained permissions. Patient location, data sensitivity, and user context determine access. Dynamic policies adapt to changing circumstances automatically.
Audit Logging and Monitoring
Comprehensive audit trails record every access to patient data. Who viewed what information and when gets permanently logged. Immutable logs prevent tampering with historical records.
Real-time monitoring detects suspicious access patterns immediately. Unusual data queries trigger automated alerts. Security teams investigate potential breaches proactively.
User behavior analytics establish baseline activity patterns. Deviations from normal behavior indicate potential threats. Machine learning models identify insider threats and compromised accounts.
Automated compliance reporting simplifies regulatory audits. Pre-built reports demonstrate HIPAA adherence. Auditors receive evidence of security controls without manual compilation.
Log aggregation centralizes security information from distributed systems. Security information and event management platforms correlate activities. Complex attack patterns become visible through unified analysis.
Retention policies preserve audit logs for required timeframes. Seven-year retention meets most regulatory requirements. Secure archival systems maintain log integrity over time.
Key Applications in Healthcare Operations
Automated Medical Coding and Billing
Medical coding translates clinical documentation into standardized codes. ICD-10, CPT, and HCPCS codes determine reimbursement amounts. Manual coding creates bottlenecks and introduces errors.
Natural language processing reads physician notes automatically. AI models extract diagnoses, procedures, and treatments. Suggested codes appear for human coder verification.
Claim scrubbing identifies potential denials before submission. Missing information and coding errors get flagged automatically. First-pass acceptance rates increase dramatically.
Revenue cycle acceleration improves organizational cash flow. Faster claim processing means quicker payments. Days in accounts receivable decrease significantly.
Compliance checking ensures proper documentation supports codes. AI systems identify insufficient medical necessity evidence. Audit risk decreases through proactive quality control.
Denial management becomes more efficient through pattern recognition. AI identifies common denial reasons across payers. Corrective actions prevent future claim rejections.
Intelligent Patient Scheduling
Appointment scheduling balances patient preferences with operational efficiency. No-show prediction models identify unreliable appointments. Overbooking strategies maximize provider utilization.
Automated reminder systems reduce missed appointments significantly. Text messages, emails, and phone calls reach patients through preferred channels. Confirmation requests trigger rescheduling workflows when needed.
Resource optimization matches appointments to available facilities and equipment. Procedure requirements get aligned with room capabilities. Double-booking of shared resources becomes impossible.
Waitlist management fills cancellation slots automatically. Patients seeking earlier appointments receive notifications immediately. Schedule gaps disappear through intelligent backfilling.
Patient routing directs individuals to appropriate care settings. Symptoms and acuity levels determine urgent care versus emergency department. Care coordination improves through smart triage.
HIPAA-compliant AI automation enables self-service scheduling portals. Patients book appointments directly without phone calls. Staff time gets redirected to complex coordination tasks.
Clinical Documentation Enhancement
Voice recognition software converts spoken words into text. Physicians dictate notes during or after patient encounters. Typing time decreases while documentation quality improves.
Ambient clinical intelligence captures natural conversations. Microphones record physician-patient interactions with consent. Relevant clinical information gets extracted automatically.
Template auto-population fills standard sections of notes. Patient demographics, medications, and allergies appear automatically. Physicians focus on unique aspects of each encounter.
Clinical decision support prompts appear within documentation workflows. Drug interaction warnings surface during prescription entry. Evidence-based order sets guide treatment decisions.
Quality measure tracking happens automatically during documentation. Physicians receive real-time feedback on performance metrics. Pay-for-performance bonuses increase through complete documentation.
Discharge summary generation compiles hospitalization information automatically. Key events, procedures, and medications get organized clearly. Continuity of care improves through comprehensive handoffs.
Predictive Analytics for Patient Care
Readmission risk models identify vulnerable patients before discharge. Social determinants, comorbidities, and prior utilization predict outcomes. Care management resources get allocated to high-risk individuals.
Sepsis prediction algorithms analyze vital signs and lab values continuously. Early warning systems alert clinicians to subtle deterioration. Intervention before clinical decline saves lives.
Fall risk assessment happens automatically using multiple data points. Age, medications, and prior falls combine in predictive models. Prevention protocols activate for high-risk patients.
Medication adherence prediction identifies non-compliant patients. Prescription fill patterns and appointment attendance inform models. Pharmacist interventions target those most likely to benefit.
Disease progression modeling forecasts patient trajectories. Chronic condition management improves through personalized predictions. Resource planning becomes more accurate.
Population health stratification groups patients by risk levels. Preventive care outreach targets appropriate populations. Healthcare costs decrease through proactive management.
Implementation Strategies for Healthcare Organizations
Conducting Privacy Impact Assessments
Privacy impact assessments identify potential risks before deployment. Data flows get mapped from source to destination. Every system touching PHI receives scrutiny.
Risk analysis evaluates likelihood and severity of privacy breaches. Technical vulnerabilities and process weaknesses get documented. Mitigation strategies address identified concerns.
Stakeholder engagement includes privacy officers and legal counsel. Clinical champions ensure solutions meet workflow needs. Information security teams validate technical controls.
Alternative analysis explores different implementation approaches. Privacy-preserving options get compared objectively. The least invasive effective solution gets selected.
Documentation requirements create permanent records of decisions. Justifications for privacy trade-offs get preserved. Regulatory audits benefit from thorough impact assessments.
Ongoing monitoring ensures assessments remain current. System changes trigger reassessment requirements. Privacy protection evolves with technology capabilities.
Building Business Associate Agreements
Business associate agreements establish legal obligations for vendors. AI platform providers must sign BAAs before accessing PHI. Contractual protections complement technical safeguards.
Permitted uses and disclosures get defined explicitly. Data processing activities require specific authorization. Vendors cannot use PHI beyond contracted purposes.
Security requirement specifications mandate minimum protections. Encryption standards, access controls, and audit logging get detailed. Performance metrics hold vendors accountable.
Breach notification obligations create incident response protocols. Discovery timelines and communication procedures get established. Coordinated response minimizes harm from security incidents.
Subcontractor management extends BAA requirements through the supply chain. Vendors must obtain satisfactory assurances from their partners. Healthcare organizations maintain oversight authority.
Termination provisions address data return or destruction. PHI must be disposed of securely after contract ends. Verification of proper deletion protects organizations.
Training Healthcare Staff
HIPAA training educates employees on privacy obligations. Annual refreshers reinforce important concepts. Role-specific training addresses job-relevant scenarios.
AI system training teaches staff how to use new tools. Hands-on practice sessions build confidence and competence. Super-users provide peer support during adoption.
Security awareness programs prevent social engineering attacks. Phishing simulations test employee vigilance. HIPAA-compliant AI automation security depends on human factors.
Incident reporting training encourages transparency. Employees learn to recognize and report potential breaches. Blameless culture promotes early detection.
Continuous education addresses evolving threats and technologies. Quarterly updates cover new risks and countermeasures. Learning management systems track completion and comprehension.
Champion development creates internal expertise. Selected staff receive advanced training. Knowledge sharing multiplies organizational capabilities.
Choosing the Right AI Vendors
Vendor evaluation begins with HIPAA compliance verification. SOC 2 Type II reports demonstrate operational security. HITRUST certification provides healthcare-specific validation.
Technical capabilities must match organizational requirements. Scalability supports growing data volumes and user populations. Integration capabilities connect with existing systems.
Customer references reveal real-world implementation experiences. Similar organizations provide relevant insights. Site visits demonstrate solutions in production environments.
Financial stability ensures long-term vendor viability. Publicly traded companies offer transparency. Private companies should share financial statements.
Product roadmap alignment prevents obsolescence. Vendors should invest in ongoing innovation. Healthcare industry commitment demonstrates staying power.
Support and service levels determine operational reliability. 24/7 technical support prevents extended outages. Dedicated account teams provide personalized attention.
Overcoming Implementation Challenges
Managing Change Resistance
Physician skepticism toward technology creates adoption barriers. Clinical workflow disruption concerns must be addressed directly. Early involvement in solution design builds buy-in.
Staff fear of job displacement requires honest communication. Automation augments rather than replaces human workers. Redeployment opportunities should be clearly articulated.
Training time constraints challenge busy healthcare workers. Microlearning modules fit into brief schedule gaps. Just-in-time training occurs within daily workflows.
Legacy system attachment stems from familiarity and comfort. Gradual transition strategies ease psychological burdens. Parallel operations provide safety nets during cutover.
Success stories from peer organizations inspire confidence. Case studies demonstrate tangible benefits. Site visits to exemplar facilities motivate change.
Leadership commitment signals organizational priority. Executive sponsorship overcomes middle management resistance. Resource allocation demonstrates serious intent.
Integrating with Legacy Systems
Health information exchange standards enable interoperability. HL7 FHIR provides modern API-based connectivity. Legacy systems often use older messaging protocols.
Interface engines translate between different data formats. Bidirectional synchronization maintains consistency across systems. Real-time updates prevent data staleness.
Data migration strategies move historical information to new platforms. Extract, transform, and load processes clean and standardize data. Validation ensures migration accuracy.
Hybrid architectures support gradual modernization. New AI capabilities coexist with legacy systems. Incremental replacement reduces risk and disruption.
API gateways provide unified access to diverse systems. Modern applications consume data through standardized interfaces. Backend complexity gets abstracted away.
HIPAA-compliant AI automation platforms offer pre-built connectors. Common EHR systems integrate with minimal custom development. Time-to-value accelerates through vendor partnerships.
Ensuring Data Quality and Accuracy
Data cleansing identifies and corrects errors in source systems. Duplicate records get merged through sophisticated matching. Standardization improves consistency across fields.
Validation rules prevent garbage data from entering systems. Format checks and range limits enforce quality standards. Real-time feedback guides users toward correct input.
Master data management creates authoritative reference sources. Patient demographics, provider directories, and drug formularies get centralized. Downstream systems consume golden records.
Data governance frameworks establish accountability and standards. Stewardship roles assign ownership for data domains. Quality metrics drive continuous improvement.
Anomaly detection flags suspicious data patterns automatically. Statistical analysis identifies outliers requiring investigation. Data quality dashboards provide visibility.
Human review validates AI-generated outputs initially. Accuracy rates improve through feedback loops. Confidence thresholds determine automation levels.
Measuring Return on Investment
Baseline metrics establish pre-implementation performance levels. Current processing times, error rates, and costs get documented. Improvement calculations require accurate starting points.
Time savings quantify efficiency gains from automation. Staff hours redirected to higher-value activities create capacity. Labor cost reductions flow directly to bottom line.
Revenue cycle improvements increase cash collections. Faster claim processing and fewer denials boost income. Days sales outstanding decrease measurably.
Quality improvements reduce costly adverse events. Fewer medication errors and hospital-acquired conditions save money. Patient satisfaction scores increase.
Compliance cost avoidance prevents regulatory penalties. Audit preparation time decreases substantially. Privacy breach risks diminish through stronger controls.
Patient experience enhancements attract and retain customers. Convenient self-service options differentiate organizations. Market share grows through superior service.
Advanced Use Cases and Innovations
AI-Powered Diagnostic Assistance
Medical imaging analysis detects abnormalities with superhuman accuracy. Chest X-rays reveal pneumonia and lung nodules reliably. Mammograms get screened for breast cancer automatically.
Pathology slide review identifies cancerous cells and tissues. Digital pathology platforms enable remote consultations. Diagnostic turnaround times decrease significantly.
Genomic analysis interprets genetic test results rapidly. Variant classification informs precision medicine decisions. Pharmacogenomics guides medication selection.
Symptom checking applications triage patient concerns appropriately. Decision trees guide patients to correct care settings. Emergency department overutilization decreases.
Differential diagnosis support suggests possible conditions. Electronic health record data feeds comprehensive assessments. Rare diseases get considered through exhaustive analysis.
Remote patient monitoring detects concerning trends early. Wearable devices stream vital signs continuously. HIPAA-compliant AI automation enables scalable chronic disease management.
Virtual Health Assistants
Conversational AI handles routine patient inquiries automatically. Appointment scheduling, prescription refills, and test results get managed. Call center volumes decrease dramatically.
Medication adherence coaching provides personalized reminders. Patients receive encouragement and education through messaging. Compliance rates improve measurably.
Pre-visit preparation guides patients through intake processes. Digital forms collect information before appointments. Check-in time decreases significantly.
Post-discharge follow-up ensures successful transitions. Automated calls assess recovery and identify complications. Readmissions decrease through proactive outreach.
Chronic disease management programs deliver education and support. Diabetes, hypertension, and heart failure patients receive regular contact. Self-management skills improve over time.
Mental health support provides accessible counseling resources. Cognitive behavioral therapy techniques get delivered digitally. Crisis detection routes urgent cases to human counselors.
Drug Discovery and Development
Molecular modeling accelerates pharmaceutical research. AI predicts drug-target interactions computationally. Promising candidates advance faster through development pipelines.
Clinical trial matching connects patients with appropriate studies. Eligibility criteria get compared against electronic health records. Recruitment timelines shorten substantially.
Adverse event detection identifies safety signals earlier. Real-world evidence supplements traditional surveillance. Patient safety improves through rapid response.
Repurposing analysis discovers new uses for existing drugs. AI identifies unexpected therapeutic applications. Development costs decrease through shortened timelines.
Precision medicine matching personalizes treatment selection. Biomarker profiles guide therapy choices. Treatment response rates improve through stratification.
Manufacturing optimization increases pharmaceutical production efficiency. Quality control gets automated through computer vision. Batch release happens faster.
Population Health Management
Social determinants of health analysis reveals community needs. Housing instability, food insecurity, and transportation barriers get identified. Interventions address root causes of poor health.
Community resource matching connects patients with support services. Food banks, housing assistance, and transportation programs get recommended. Holistic care coordination emerges.
Outbreak prediction models forecast disease spread patterns. Syndromic surveillance identifies emerging threats early. Public health response activates proactively.
Health equity analysis reveals disparities in care delivery. Demographic patterns highlight underserved populations. Targeted outreach reduces inequality.
Cost prediction helps organizations manage financial risk. High-cost patient identification enables intervention. Total cost of care decreases through prevention.
Quality improvement initiatives benefit from comprehensive analytics. Performance variation between providers gets quantified. Best practice sharing elevates entire organizations.
Regulatory Compliance and Governance
Maintaining Ongoing HIPAA Compliance
Regular risk assessments identify emerging vulnerabilities. Annual security reviews examine technical and administrative controls. Continuous monitoring detects deviations from baselines.
Policy updates reflect changing regulations and technologies. HIPAA guidelines evolve with healthcare landscape. Documentation maintains current compliance posture.
Incident response testing validates breach procedures. Tabletop exercises simulate various scenarios. Response times improve through practice.
Vendor management programs oversee business associates. Annual assessments verify ongoing compliance. Corrective action plans address deficiencies.
Sanctions policies hold employees accountable for violations. Progressive discipline reinforces expectations. Termination occurs for egregious breaches.
Breach notification procedures ensure timely reporting. Templates expedite required communications. Legal review prevents missteps.
FDA Regulations for Medical AI
Software as a medical device designation applies to diagnostic AI. FDA clearance or approval becomes necessary. Clinical validation demonstrates safety and efficacy.
Quality management systems govern medical device development. Design controls ensure products meet specifications. Risk management identifies and mitigates hazards.
Post-market surveillance monitors real-world performance. Adverse event reporting captures safety concerns. Product improvements address identified issues.
Algorithm transparency requirements demand explainability. Black box models face regulatory skepticism. HIPAA-compliant AI automation in diagnostics needs interpretability.
Clinical trial design for AI differs from drug studies. Performance metrics replace traditional endpoints. Validation datasets require careful curation.
Regulatory pathways vary by risk classification. De novo submissions create new device categories. Premarket approvals apply to high-risk devices.
State Privacy Laws and International Standards
California Consumer Privacy Act grants additional patient rights. Healthcare data receives special protections. Compliance requires expanded capabilities.
European General Data Protection Regulation affects multinational organizations. Data processing agreements must meet GDPR standards. Cross-border transfers require safeguards.
State breach notification laws vary in requirements. Notification triggers and timelines differ by jurisdiction. Compliance teams must track multiple regimes.
International data localization rules restrict cloud deployments. Some countries require data to remain within borders. Architecture decisions accommodate geographic constraints.
Industry frameworks complement regulatory requirements. HITRUST Common Security Framework provides comprehensive guidance. Certification demonstrates maturity.
Accreditation standards raise operational bars. Joint Commission and NCQA have specific requirements. HIPAA-compliant AI automation must support accreditation goals.
Future Trends in Healthcare AI
Federated Learning and Privacy-Preserving AI
Federated learning trains models without centralizing data. Algorithms travel to data rather than vice versa. Patient privacy gets enhanced through distributed computing.
Differential privacy adds mathematical guarantees to protections. Individual records cannot be reverse-engineered from outputs. Privacy-utility trade-offs get optimized.
Homomorphic encryption enables computation on encrypted data. Sensitive information never gets decrypted during processing. Breakthrough capabilities emerge from cryptographic advances.
Secure multi-party computation allows collaborative analysis. Competing organizations share insights without exposing data. Population-level studies become possible.
Synthetic data generation creates realistic training datasets. Statistical properties match real data without actual patients. Development and testing happen safely.
Zero-knowledge proofs verify facts without revealing details. Credentials get validated without exposing underlying information. Authentication becomes privacy-preserving.
Quantum Computing Implications
Quantum computers threaten current encryption standards. Post-quantum cryptography prepares for this future. Healthcare organizations must plan transitions.
Quantum machine learning promises computational advantages. Drug discovery and genomic analysis could accelerate dramatically. Healthcare applications remain largely theoretical.
Optimization problems benefit from quantum approaches. Resource scheduling and treatment planning could improve. Practical quantum advantage remains years away.
Security implications demand immediate attention. Current PHI encryption will become vulnerable eventually. Long-term data protection requires planning now.
Hybrid quantum-classical systems will emerge first. Quantum processors handle specific subtasks. HIPAA-compliant AI automation will adapt gradually.
Standards development happens through industry collaboration. NIST leads post-quantum cryptography efforts. Healthcare sector must engage actively.
Personalized Medicine Revolution
Genomic medicine integrates genetic information into care. Inherited disease risks inform screening recommendations. Treatment selection becomes DNA-guided.
Proteomics and metabolomics add molecular detail. Multi-omics integration creates comprehensive profiles. Precision increases through layered analysis.
Digital twins simulate individual patient physiology. Treatment effects get predicted before administration. Trial-and-error medicine becomes obsolete.
Continuous monitoring through wearables provides real-time data. AI analyzes streams for concerning patterns. Interventions happen at optimal moments.
Behavioral phenotyping characterizes individual patterns. Activity, sleep, and social interactions inform care. Mental health treatment becomes highly personalized.
N-of-1 trials test treatments in single patients. Individual response guides therapy selection. Evidence-based medicine becomes patient-specific.
Frequently Asked Questions
What makes AI automation HIPAA-compliant?
HIPAA compliance requires comprehensive security controls. Encryption, access controls, and audit logging provide technical safeguards. Administrative policies govern employee behavior and vendor relationships.
Business associate agreements establish legal obligations. AI vendors must contractually commit to privacy protection. Regular audits verify ongoing compliance.
Can small healthcare practices afford AI automation?
Cloud-based solutions offer subscription pricing models. Small practices pay only for actual usage. Capital investment requirements decrease substantially.
Vendor ecosystems provide pre-built integrations. Electronic health record companies offer AI modules. Bundled solutions reduce implementation complexity.
How accurate are AI diagnostic tools?
Accuracy varies by specific application and implementation. FDA-cleared devices meet rigorous validation standards. Diagnostic accuracy often exceeds human performance.
Ongoing monitoring ensures maintained performance. Real-world accuracy gets tracked continuously. Model updates address degradation over time.
Will AI replace healthcare workers?
AI augments rather than replaces human clinicians. Routine tasks get automated while complex decisions remain human. Job roles evolve toward higher-value activities.
New positions emerge around AI management. Clinical informaticists and data scientists join care teams. Employment shifts rather than disappears.
How long does implementation take?
Simple automation projects deploy in weeks. Complex enterprise implementations require 6-12 months. Phased approaches balance speed and thoroughness.
Vendor experience accelerates timelines significantly. Established platforms have proven methodologies. Custom development extends schedules.
What about patients who lack digital access?
Digital divide concerns require thoughtful solutions. Multiple access channels accommodate varying capabilities. Traditional options remain available alongside automation.
Assistance programs provide devices and training. Community partnerships extend digital reach. HIPAA-compliant AI automation complements rather than replaces human interaction.
How do you handle AI errors in clinical settings?
Human oversight catches AI mistakes before patient harm. Confidence thresholds route uncertain cases to clinicians. Quality assurance monitors error rates.
Incident reporting captures failures systematically. Root cause analysis informs improvements. Continuous learning prevents repeated mistakes.
What ROI can organizations expect?
Return on investment varies by application area. Revenue cycle improvements show fastest payback. Clinical quality benefits accrue gradually.
Typical payback periods range from 12-36 months. Ongoing value compounds over time. Strategic advantages extend beyond financial metrics.
Read More:-5 Steps to Connect Your Internal Database to a Private LLM
Conclusion

HIPAA-compliant AI automation transforms healthcare delivery fundamentally. Patient care improves while administrative burdens decrease. Regulatory requirements get satisfied through thoughtful implementation.
Healthcare organizations face complex technology decisions. Balancing innovation with privacy protection requires expertise. Comprehensive strategies address technical, legal, and operational dimensions.
Security controls form the foundation of compliant systems. Encryption, access management, and audit logging protect patient data. Business associate agreements extend protections through vendor relationships.
Clinical applications demonstrate remarkable capabilities. Diagnostic assistance, predictive analytics, and virtual care expand rapidly. Patient outcomes improve through data-driven insights.
Operational efficiency gains free resources for patient care. Revenue cycle acceleration improves financial performance. Staff satisfaction increases as tedious work disappears.
Implementation challenges demand careful management. Change resistance, legacy integration, and data quality require attention. Leadership commitment enables successful transformation.
Regulatory compliance evolves with technology capabilities. HIPAA, FDA, and state privacy laws create complex requirements. Proactive governance maintains ongoing adherence.
Future innovations promise even greater capabilities. Federated learning and quantum computing will reshape possibilities. Personalized medicine becomes reality through AI advancement.
HIPAA-compliant AI automation represents the future of healthcare. Organizations that embrace these technologies gain competitive advantages. Patient care reaches new levels of quality and accessibility.
Investment in compliant AI systems delivers lasting value. Financial returns justify implementation costs. Strategic positioning ensures long-term viability.
The healthcare industry stands at a transformation inflection point. AI automation enables previously impossible capabilities. HIPAA-compliant AI automation makes this revolution both powerful and safe.