Introduction
TL;DR Voice calls have always been deeply personal. The human voice carries emotion, urgency, and vulnerability. Now artificial intelligence enters this intimate space. The question isn’t whether AI can handle voice calls. The real challenge involves teaching machines to recognize and respond to human emotions authentically.
Empathetic AI in voice calls represents the next frontier in customer service and personal assistance. Companies invest billions developing systems that don’t just hear words. These technologies aim to understand feelings. AI listening behavior in voice assistants must evolve beyond simple command recognition. The future demands emotional intelligence at scale.
Table of Contents
Understanding Empathy in Artificial Intelligence
Empathy means recognizing and responding appropriately to emotions. Humans develop this skill through years of social interaction. We read facial expressions, body language, and vocal cues. Machines lack this intuitive understanding. They must learn empathy through data and algorithms.
True empathy involves multiple components. Cognitive empathy means understanding another person’s perspective. Emotional empathy involves feeling what others feel. Compassionate empathy drives helpful action. AI attempts to replicate these dimensions through technology.
Current voice assistants handle transactional requests well. They set timers, check weather, and answer factual questions. Emotional nuance remains largely absent. A frustrated user gets the same robotic response as a delighted one. This limitation creates unsatisfying experiences during sensitive interactions.
The Gap Between Recognition and Response
AI can detect emotional signals with increasing accuracy. Voice analysis reveals stress, anger, sadness, and joy. Pitch, tempo, volume, and vocal quality provide emotional clues. Modern systems achieve 70-80% accuracy identifying basic emotions from speech alone.
Recognition alone doesn’t create empathetic interactions. The system must respond appropriately to detected emotions. An angry customer needs de-escalation techniques. A confused caller requires patient explanation. A grieving person deserves gentle compassion. Matching response to emotion remains technically challenging.
Context determines appropriate emotional responses. The same sadness might need different approaches in different situations. Grief over a lost package differs dramatically from bereavement. AI listening behavior in voice assistants must incorporate situational awareness. This contextual understanding separates mechanical emotion detection from genuine empathy.
Why Empathy Matters in Voice Communication
Voice calls handle our most important and sensitive matters. People call doctors about health scares. They contact banks during financial emergencies. Customer service receives complaints about failed products at critical moments. These interactions carry emotional weight.
Empathy reduces stress during difficult conversations. Feeling understood calms anxious callers. Appropriate emotional responses build trust quickly. People cooperate more when they feel heard. Studies show empathetic service recovery increases customer loyalty by 40%.
The absence of empathy damages relationships irreparably. Robotic responses during emotional moments feel dismissive. Customers abandon companies that show no understanding. Healthcare patients lose trust in systems that seem cold. The emotional dimension of voice communication cannot be ignored.
Voice carries more emotional information than text. Written messages lack tone and inflection. People misinterpret emails constantly. Voice communication provides rich emotional data. AI systems must leverage this information to create authentic connections.
Current State of Emotional AI Technology
Several companies lead the race toward empathetic AI. Affectiva pioneered emotion recognition from faces and voices. Cogito guides human agents with real-time emotional intelligence. Hume AI focuses specifically on vocal expression understanding. These companies demonstrate commercial viability of emotional technology.
Speech emotion recognition analyzes acoustic features. Machine learning models extract pitch contours, energy levels, and spectral characteristics. These features correlate with emotional states. Algorithms learn patterns from thousands of labeled voice samples. Accuracy improves as training datasets grow.
Sentiment analysis processes the actual words spoken. Natural language processing identifies emotionally charged terms. “Frustrated,” “disappointed,” and “angry” signal negative sentiment. “Thrilled,” “grateful,” and “satisfied” indicate positive feelings. Combining acoustic analysis with linguistic content provides fuller emotional pictures.
Machine Learning Approaches
Supervised learning requires labeled emotional data. Researchers record actors expressing specific emotions. They collect real customer service calls with emotion tags. Models train on these examples. The system learns which acoustic patterns correspond to which feelings. Accuracy depends entirely on training data quality and diversity.
Deep learning networks process raw audio directly. Convolutional neural networks extract relevant features automatically. Recurrent networks capture emotional changes over time. Attention mechanisms focus on emotionally significant moments. These architectures achieve state-of-the-art performance on emotion recognition benchmarks.
Transfer learning accelerates development. Models pre-trained on large speech datasets adapt to emotion recognition. This approach requires less labeled emotional data. Performance improves while reducing development costs. Companies without massive datasets can still build effective systems.
Multimodal fusion combines voice with other signals. Video adds facial expressions. Text provides linguistic content. Physiological sensors measure heart rate and skin conductance. Integrating multiple channels improves accuracy significantly. AI listening behavior in voice assistants benefits from this comprehensive approach.
Real-World Implementations
Mental health applications use empathetic AI today. Therapy chatbots detect depression and anxiety from voice patterns. They adjust conversation tone based on emotional state. Crisis hotlines employ AI screening to prioritize urgent cases. These systems save lives by recognizing emotional distress early.
Call centers deploy emotion detection widely. Supervisors receive alerts when customers become angry. Systems route emotionally charged calls to experienced agents. Quality assurance reviews flag interactions lacking empathy. These tools improve service quality and customer satisfaction measurably.
Healthcare providers implement empathetic virtual assistants. Patients describe symptoms with natural emotion. The AI responds with appropriate concern and reassurance. Appointment scheduling adapts to patient urgency and anxiety levels. This technology improves patient experience while reducing administrative burden.
Education platforms use emotion recognition for adaptive learning. Students express frustration when stuck on concepts. AI tutors detect this emotion and adjust teaching approaches. Encouragement increases when confidence drops. Emotional awareness personalizes education effectively.
Technical Challenges in Building Empathetic Systems
Emotion varies enormously across cultures. Vocal expressions of anger differ between Japanese and Italian speakers. What sounds enthusiastic in one culture seems aggressive in another. AI listening behavior in voice assistants must account for cultural diversity. Training on predominantly Western data creates biased systems.
Individual differences complicate emotion recognition. Some people speak expressively with dramatic vocal variation. Others maintain flat affect regardless of feelings. Personality, gender, and age all influence emotional expression. One-size-fits-all models fail to capture this diversity.
Sarcasm and irony break most emotion detection systems. The words say one thing. The tone conveys the opposite. “Oh great, just what I needed” might indicate frustration despite positive words. Humans detect sarcasm through subtle cues. Teaching machines this nuance remains extremely difficult.
Privacy and Ethical Considerations
Emotion detection raises serious privacy concerns. Voice analysis reveals intimate psychological states. People may not consent to this level of scrutiny. Recording and analyzing emotional patterns feels invasive. Regulations don’t yet address these specific privacy issues adequately.
Emotional manipulation becomes possible with empathetic AI. Systems could exploit detected vulnerabilities. An anxious customer might accept unfavorable terms. A lonely person could be manipulated through artificial friendship. Clear ethical guidelines must prevent these abuses.
Bias in emotion recognition harms marginalized groups. Systems trained primarily on white male voices perform worse on women and minorities. Cultural differences in emotional expression compound these biases. Deploying biased systems perpetuates discrimination. Rigorous fairness testing must precede any deployment.
Consent mechanisms need careful design. Users should know when systems analyze emotions. They deserve control over this sensitive data. Opt-out options must be genuinely accessible. Transparency about emotional AI builds necessary trust.
The Role of AI Listening Behavior in Empathetic Responses
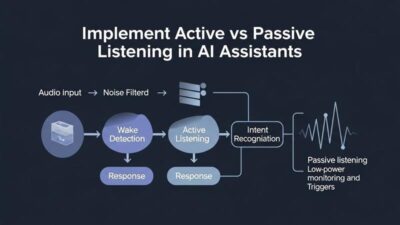
Effective empathy requires exceptional listening. Humans demonstrate empathy partly through attentive listening behaviors. They maintain focus, ask clarifying questions, and reflect understanding. AI must replicate these behaviors to seem genuinely empathetic.
Active listening involves multiple techniques. Reflecting back what someone said shows attention. “It sounds like you’re frustrated with the delay” demonstrates understanding. Validating emotions makes people feel heard. “I understand why that would be upsetting” acknowledges feelings legitimately.
Appropriate timing matters enormously. Interrupting someone mid-sentence feels dismissive. Waiting too long creates awkward silences. AI listening behavior in voice assistants must include sophisticated turn-taking. The system should sense when to speak and when to remain quiet.
Designing Natural Conversational Flow
Empathetic conversations follow organic patterns. Humans don’t respond instantly with solutions. They acknowledge emotions first. “I’m sorry to hear that” precedes problem-solving. AI must learn this emotional sequencing. Jumping straight to solutions seems cold and mechanical.
Pacing adjusts to emotional intensity. Excited callers appreciate matching enthusiasm. Distressed people need slower, calmer responses. The AI should modulate speech rate and energy. This mirroring creates rapport naturally.
Silence serves important functions. Brief pauses show thoughtfulness. They give people space to collect thoughts. Strategic silence communicates respect. AI systems typically fear dead air. Teaching machines when silence helps represents a significant design challenge.
Backchanneling provides continuous feedback. “Mm-hmm,” “I see,” and “go on” keep conversations flowing. These small acknowledgments show active listening. AI listening behavior in voice assistants should include natural backchannels. The timing and variety must feel authentic rather than scripted.
Emotional Memory Across Interactions
Remembering emotional context improves relationships. A customer who called angry yesterday needs acknowledgment today. “I hope we resolved your concern from yesterday” shows continuity. This memory transforms transactional exchanges into ongoing relationships.
Long-term emotional tracking reveals patterns. Someone frequently calling while stressed might need additional support. Detecting escalating frustration enables proactive intervention. Healthcare applications particularly benefit from longitudinal emotional monitoring.
Privacy constraints limit emotional memory. Storing emotional profiles creates security risks. Data breaches exposing emotional histories would be devastating. Systems must balance useful memory with appropriate data minimization. Temporary emotional context differs from permanent psychological profiling.
User control over emotional memory remains essential. People should know what the system remembers. They deserve the ability to delete emotional data. Transparent memory policies prevent creepy surveillance feelings. AI listening behavior in voice assistants must respect these boundaries.
Future Developments in Empathetic Voice AI
Multimodal emotion recognition will become standard. Video calls combine facial expressions with voice. Wearables add physiological data. Text messages provide additional context. Integrating these channels creates comprehensive emotional understanding. Accuracy and nuance will improve dramatically.
Real-time emotion coaching will guide human agents. AI monitors conversations and suggests empathetic responses. Agents receive prompts like “customer seems frustrated, acknowledge this.” Training improves through immediate feedback. This hybrid approach combines AI insight with human authenticity.
Proactive emotional support will anticipate needs. The system detects rising frustration before customers complain. It offers help preemptively. “You seem to be having trouble, would you like assistance?” prevents problems from escalating. This anticipatory empathy feels remarkably thoughtful.
Personalized Emotional Profiles
AI will learn individual emotional patterns. Some people always sound stressed. Others remain calm during crises. Personalized baselines improve emotion detection accuracy. The system distinguishes genuine distress from normal speaking style.
Preference learning adapts interaction styles. Some people want efficiency over warmth. Others need extensive emotional support. The AI learns which approach each person prefers. Conversations optimize for individual communication styles.
Cultural adaptation will handle global diversity. The system recognizes cultural communication norms. It adjusts emotional interpretations accordingly. Response styles match cultural expectations. This cultural intelligence makes AI genuinely global rather than Western-centric.
Relationship building through repeated interactions creates familiarity. The AI develops rapport over time. Callbacks to previous conversations strengthen connections. “Last time you mentioned…” shows genuine attention. These accumulated interactions feel increasingly human-like.
Integration With Advanced Technologies
Generative AI will create emotionally appropriate responses. Large language models already produce natural language. Adding emotional conditioning generates empathetic replies. The system crafts responses matching both content needs and emotional tone. This flexibility surpasses pre-scripted responses dramatically.
Voice synthesis will convey authentic emotion. Current text-to-speech sounds neutral or cheerful. Future systems will generate concerned, sympathetic, or excited voices. Prosody, pitch, and timing will match intended emotions. AI listening behavior in voice assistants will pair with emotionally expressive speech.
Virtual reality integration adds visual empathy cues. Avatar faces express appropriate emotions during calls. Body language reinforces vocal empathy. This multisensory approach creates presence and connection. Healthcare and therapy applications will particularly benefit.
Brain-computer interfaces represent the distant frontier. Direct neural signals could bypass voice entirely. Thoughts and feelings might transfer directly. This technology remains largely theoretical. Ethical implications require extensive consideration before any implementation.
Industry-Specific Applications and Impact
Healthcare stands to gain enormously from empathetic AI. Doctor-patient relationships depend on trust and understanding. AI assistants could provide emotional support between appointments. They monitor mental health through voice patterns. Early intervention becomes possible through continuous emotional tracking.
Telemedicine benefits particularly from empathetic technology. Remote consultations lack in-person warmth. Empathetic AI compensates for physical distance. Patients feel cared for despite geographic separation. This technology enables quality healthcare in underserved areas.
Mental health treatment uses empathetic AI extensively. Therapy chatbots provide 24/7 emotional support. They detect suicidal ideation from voice cues. Crisis intervention activates automatically. These systems extend mental health resources significantly.
Customer Service Evolution
Contact centers transform through empathetic AI. Customer satisfaction increases when people feel understood. First-call resolution improves with emotional awareness. Agents supported by emotional AI perform better. Companies see measurable ROI from empathy investments.
Complaint handling becomes less adversarial. Acknowledging customer frustration defuses anger. Empathetic responses convert critics into advocates. Service recovery strengthens relationships when done well. AI listening behavior in voice assistants enables consistent empathy at scale.
Sales conversations benefit from emotional intelligence. Detecting buying signals improves conversion rates. Recognizing hesitation prompts appropriate reassurance. Pushy approaches back off when customers feel pressured. Empathetic selling respects customer emotions while achieving business goals.
Retention programs use emotional insights strategically. Detecting dissatisfaction triggers retention offers. Emotional engagement predicts churn risk. Proactive outreach to emotionally distant customers saves relationships. These interventions work because they address underlying feelings.
Education and Training
Virtual tutors adapt to student emotions. Frustration signals when to slow down. Boredom indicates need for engagement. Confidence suggests readiness for harder challenges. Emotional responsiveness personalizes education powerfully.
Language learning benefits from empathetic practice partners. AI conversation partners provide patient, judgment-free practice. They encourage nervous speakers. Pronunciation correction comes with supportive feedback. This emotional safety accelerates learning.
Corporate training uses emotionally intelligent simulations. Leadership scenarios require empathetic responses. The AI plays different emotional roles realistically. Trainees practice handling difficult emotional situations safely. This preparation improves real-world performance.
Special education applications support neurodivergent students. Autistic individuals often struggle reading emotions. AI can label emotions explicitly during conversations. This scaffolding develops emotional skills gradually. Technology provides patient, consistent emotional education.
Building Trust in Empathetic AI Systems
Transparency about AI capabilities prevents disappointment. Users should know they’re interacting with machines. Pretending to be human feels deceptive. Clear disclosure builds appropriate expectations. People accept AI limitations when honestly communicated.
Explainability helps users understand AI decisions. Why did the system think someone sounded angry? What vocal cues triggered that interpretation? Transparency about emotional reasoning builds trust. Black-box emotion detection feels manipulative.
Human oversight remains essential for sensitive interactions. Critical emotional situations need human judgment. Suicidal callers should reach human counselors. Grief requires human compassion. AI listening behavior in voice assistants should recognize when to transfer to humans.
Performance Standards and Accountability
Accuracy benchmarks ensure minimum quality. Emotion recognition should meet specific thresholds before deployment. Regular testing catches performance degradation. Independent audits verify accuracy claims. These standards protect users from substandard systems.
Bias testing must be mandatory. Systems must perform equally across demographics. Regular fairness audits identify discriminatory patterns. Remediation addresses biases before they cause harm. This vigilance prevents AI from amplifying societal inequities.
Error handling deserves special attention. Emotion recognition will make mistakes. How systems handle misinterpretation matters enormously. Acknowledging uncertainty shows appropriate humility. “I might be misreading this” respects human complexity.
User feedback mechanisms enable continuous improvement. People should easily report inappropriate responses. These reports identify failure patterns. Developers fix systematic issues. Community input creates better systems through collective wisdom.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does AI detect emotions from voice calls?
AI analyzes acoustic features like pitch, volume, speaking rate, and voice quality. Machine learning models match these patterns to emotional states. The system also examines word choice and linguistic patterns. Combining acoustic and linguistic analysis provides comprehensive emotion detection. Accuracy reaches 70-80% for basic emotions. Complex or mixed emotions remain more challenging. Cultural and individual differences affect performance. AI listening behavior in voice assistants continues improving through better training data.
Can empathetic AI replace human customer service agents?
Current technology cannot fully replace human empathy. AI handles routine emotional interactions well. Complex situations still need human judgment. Hybrid models work best for now. AI supports human agents with emotional insights. It manages simple cases independently. Sensitive matters always escalate to humans. This division optimizes both efficiency and quality. Future AI may handle more complex empathy. Complete replacement seems unlikely for decades.
Is emotional AI safe and private?
Privacy depends on implementation choices. Responsible systems analyze emotions in real-time without storing voice data. They extract minimal emotional context. Users should have clear consent and control mechanisms. Unfortunately, some implementations are more invasive. Regulations don’t adequately protect emotional data yet. Users should research specific systems carefully. Companies must prioritize privacy in design. Strong encryption and data minimization are essential. Transparency about data handling builds necessary trust.
How accurate is AI at recognizing emotions?
Accuracy varies by emotion and context. Basic emotions like anger, happiness, and sadness reach 70-80% accuracy. Subtle emotions remain harder to detect. Cultural and individual differences reduce accuracy. Controlled laboratory conditions show better performance than real-world complexity. Sarcasm and mixed emotions challenge systems significantly. AI listening behavior in voice assistants improves constantly. Multimodal approaches combining voice, text, and video perform better. Perfect accuracy remains impossible given human emotional complexity.
What industries benefit most from empathetic AI?
Healthcare sees enormous benefits. Patient communication improves dramatically. Mental health support extends through AI companions. Telemedicine becomes more personal. Customer service transforms through emotional awareness. Banks, telecom, and retail all deploy empathetic systems. Education personalizes to student emotional states. Sales conversations respect customer feelings. Human resources uses emotional AI for employee support. Any industry involving emotional human interaction benefits significantly.
Can AI learn to feel emotions or just simulate them?
AI does not experience emotions subjectively. Current systems recognize and simulate emotional responses. They process patterns without feeling. This distinction matters philosophically. Functionally, sophisticated simulation may be indistinguishable from feeling. Users benefit from appropriate emotional responses regardless of subjective experience. Whether machines could ever truly feel remains debated. Current technology focuses on useful emotional intelligence. Phenomenological questions can wait for philosophical resolution.
How do you know if you’re talking to empathetic AI or a human?
Disclosure should always be clear. Ethical systems identify themselves as AI. Practically, detection can be difficult. Highly advanced AI sounds remarkably human. Some tells include perfect consistency and infinite patience. AI never gets tired or distracted. Responses might seem slightly scripted. Complex emotional situations reveal limitations. Asking directly usually gets honest answers. AI listening behavior in voice assistants improves constantly. The distinction will blur further. Transparency rather than detection matters most ethically.
Read More:-How Conversational Fluency Impacts User Engagement in AI
Conclusion

Empathetic AI in voice calls represents a genuine revolution in human-computer interaction. Technology finally addresses the emotional dimension of communication. This advancement transforms customer service, healthcare, education, and countless other fields. The potential benefits justify the substantial technical challenges.
Current systems demonstrate impressive capabilities. Emotion recognition achieves practical accuracy. Appropriate responses create satisfying interactions. Real-world deployments show measurable improvements in customer satisfaction. The technology works today despite remaining limitations.
Significant challenges still require solutions. Cultural bias must be eliminated. Privacy protections need strengthening. Ethical guidelines must prevent manipulation. These concerns demand serious attention. Responsible development balances innovation with safety.
The future promises even more sophisticated empathy. Multimodal sensing will provide richer emotional understanding. Personalization will adapt to individual communication styles. Generative AI will craft perfectly appropriate responses. These advances will make machine empathy nearly indistinguishable from human compassion.
AI listening behavior in voice assistants will become the standard for quality. Companies that master emotional intelligence will dominate their industries. Users will expect empathetic interactions universally. Cold, transactional systems will seem hopelessly outdated. The market will reward emotional sophistication.
Human-AI collaboration creates the most powerful approach. Technology handles scale and consistency. Humans provide judgment and authentic connection. This partnership leverages the strengths of both. Neither alone achieves what they accomplish together.
Trust depends on transparency and performance. Users must know when they interact with AI. Systems must work reliably and fairly. Privacy protections must be genuine. These foundations enable widespread adoption. Without trust, even perfect technology fails.
The path forward requires continued research investment. Emotion AI remains nascent despite impressive progress. Many technical problems need solutions. Interdisciplinary collaboration accelerates development. Combining psychology, linguistics, and computer science creates breakthroughs.
Regulatory frameworks must evolve with the technology. Current laws don’t address emotional AI adequately. Policymakers need to understand both capabilities and risks. Balanced regulation protects users without stifling innovation. This equilibrium requires ongoing dialogue.
Education about emotional AI empowers users. People should understand how these systems work. Knowledge enables informed consent decisions. Awareness of limitations prevents overreliance. A well-informed public makes better technology choices.
Empathetic AI will reshape how humans interact with technology fundamentally. Voice calls will feel natural and supportive. Emotional understanding will be ubiquitous. This transformation promises more humane digital experiences. The future of voice communication looks remarkably empathetic.