Introduction
TL;DR Private language models have transformed how organizations handle sensitive data. Businesses now want AI capabilities without compromising security. The challenge lies in safely connecting proprietary databases to these models.
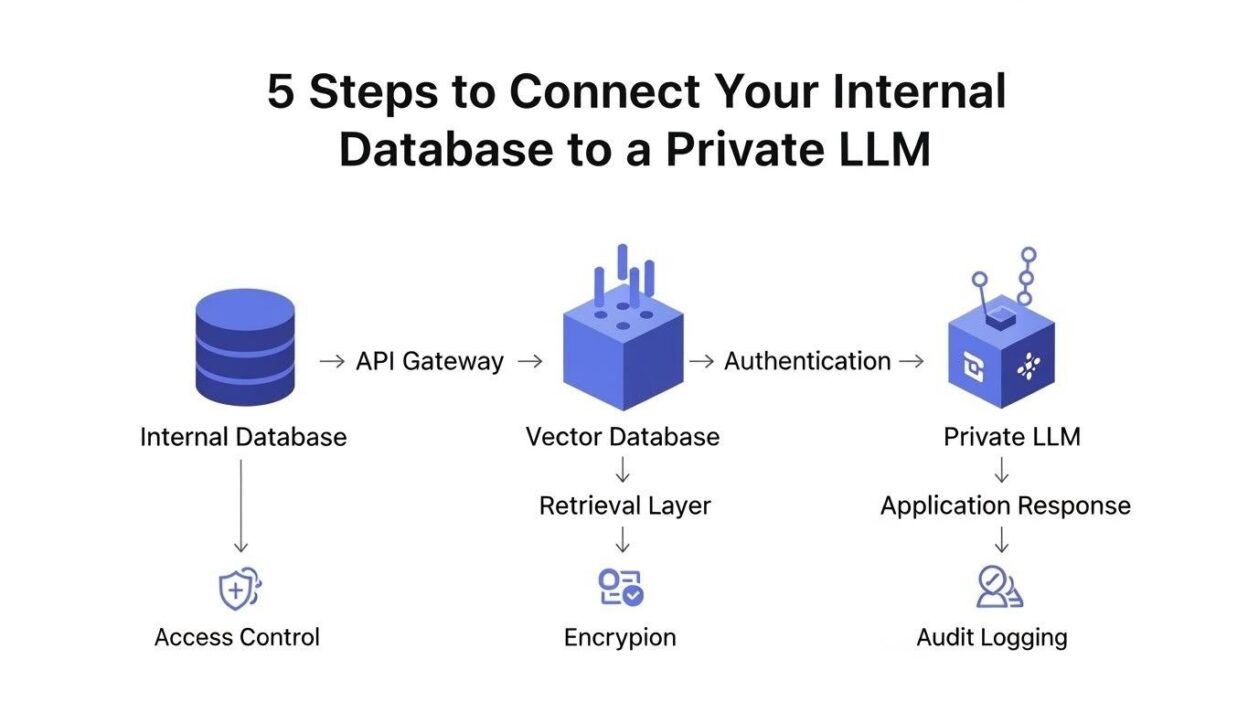
Learning how to Connect Internal Database to Private LLM systems unlocks powerful possibilities. Your organization gains AI-powered insights while maintaining data control. This guide walks through the essential process step by step.
Many companies hesitate due to technical complexity. The fear of data exposure holds teams back. Understanding the proper connection methodology eliminates these concerns. Your internal data deserves protection while delivering maximum value.
Table of Contents
Understanding Private LLMs and Database Integration
The foundation of secure AI implementation starts with knowledge. Private language models differ significantly from public alternatives. These systems operate within your controlled environment.
What Makes a Private LLM Different
Private LLMs run on infrastructure you control directly. They never send data to external servers. Your information stays within organizational boundaries. This architecture protects intellectual property and customer data.
Organizations deploy private models on-premises or in isolated cloud environments. The models process queries without internet connectivity requirements. Training happens on your specific datasets exclusively. This specialization improves accuracy for domain-specific tasks.
Public LLMs like ChatGPT operate on shared infrastructure. Your queries travel to external servers for processing. The provider potentially sees all input data. Privacy policies govern usage but don’t guarantee complete isolation.
Why Database Connectivity Matters
Internal databases contain your most valuable information. Customer records, financial data, and operational metrics live here. AI models need access to this information for meaningful analysis.
Direct database connectivity enables real-time insights. The LLM queries current data rather than outdated exports. Decision-making improves through access to live information. Analytics become more accurate and actionable.
Manual data transfer creates security vulnerabilities. Employees might export sensitive files unnecessarily. Automated connections reduce human error risks. The system maintains audit trails for compliance purposes.
Common Use Cases for Connected Systems
Customer service teams use connected LLMs for instant information retrieval. The AI accesses customer histories and provides personalized responses. Support quality improves while resolution times decrease.
Financial analysts query databases through natural language. Complex SQL becomes unnecessary for basic reporting. The LLM translates questions into proper database queries. Insights arrive faster without specialized technical skills.
Product teams analyze user behavior patterns efficiently. The AI identifies trends across massive datasets quickly. Recommendations emerge from comprehensive data analysis. Innovation accelerates through better information access.
Step 1: Prepare Your Database Infrastructure
Proper preparation prevents security issues and performance problems. Your database needs optimization before LLM integration. This groundwork ensures smooth operation later.
Assess Your Current Database Architecture
Document your existing database structure thoroughly. Identify all tables, relationships, and data types. Understanding the schema helps plan integration points. Security requirements vary across different data categories.
Evaluate current access controls and permissions. Review who can query specific tables. Audit existing security policies for gaps. The LLM will need appropriate access levels without excessive privileges.
Check database performance under current loads. Measure query response times and resource usage. Additional AI queries will increase demand. Your infrastructure must handle the extra workload.
Implement Proper Access Controls
Create dedicated database user accounts for LLM access. Never use administrative credentials for AI connections. Limit permissions to necessary tables only. This principle of least privilege minimizes damage from potential breaches.
Configure row-level security where appropriate. The LLM should only access authorized data. Customer information might require geographic restrictions. Compliance frameworks often mandate granular access controls.
Set up detailed logging for all database interactions. Track every query the LLM executes. Monitoring helps detect unusual access patterns. Audit logs prove essential for regulatory compliance.
Optimize Database Performance
Index frequently queried columns before integration. The LLM will generate numerous database queries. Proper indexing dramatically improves response times. Slow queries frustrate users and waste resources.
Partition large tables for better performance. Historical data might move to separate partitions. The LLM accesses recent information more frequently. This structure balances speed with completeness.
Configure connection pooling to handle concurrent requests. Multiple users might query the LLM simultaneously. Database connection limits could create bottlenecks. Pooling ensures efficient resource utilization.
Establish Data Quality Standards
Clean your data before connecting AI systems. Inconsistent formats confuse language models. Duplicate records produce incorrect analysis results. Data quality directly impacts AI accuracy.
Standardize naming conventions across tables. The LLM learns patterns from your schema. Clear, consistent names improve understanding. Abbreviations and codes need proper documentation.
Implement validation rules for new data entry. Preventing bad data proves easier than fixing it later. Quality gates maintain database integrity. The LLM generates better insights from clean information.
Step 2: Choose the Right Private LLM Solution
Selecting an appropriate model affects everything downstream. Different private LLMs offer varying capabilities. Your specific needs should guide this decision.
Evaluate On-Premises vs Cloud-Hosted Options
On-premises deployments provide maximum control and security. The model runs entirely within your data center. No external network access occurs during operation. Highly regulated industries often require this approach.
Cloud-hosted private instances offer easier management. Major providers offer isolated LLM environments. Your data never mixes with other customers. Scalability becomes simpler than physical hardware.
Hybrid approaches combine both deployment methods. Development happens in the cloud for flexibility. Production runs on-premises for security. This balance suits many organizational needs.
Compare Popular Private LLM Platforms
LLaMA models from Meta offer strong open-source options. Organizations can deploy these freely on their infrastructure. The community provides extensive documentation and support. Customization possibilities remain nearly unlimited.
GPT-4 through Azure OpenAI provides enterprise-grade capabilities. Microsoft offers private deployments with strict data controls. Performance matches public versions without privacy concerns. Pricing reflects the premium service level.
Anthropic’s Claude offers private deployment options for enterprises. The model excels at nuanced reasoning tasks. Safety features align with corporate governance needs. Integration requires working with Anthropic directly.
Mistral AI delivers efficient European-developed models. Smaller parameter counts reduce hardware requirements. Performance remains competitive with larger models. GDPR compliance comes built into the platform.
Consider Model Size and Hardware Requirements
Larger models generally perform better on complex tasks. They understand context more deeply and reason better. The tradeoff comes in computational resources needed. Your hardware must support the chosen model size.
7B parameter models run on modest server hardware. They handle straightforward queries adequately. Resource efficiency makes them attractive for budget-conscious deployments. Accuracy might suffer on specialized tasks.
13B to 70B parameter models require substantial GPU resources. They deliver professional-grade performance across domains. Most enterprises find this range offers the best balance. Investment in proper hardware pays dividends.
175B+ parameter models demand extensive infrastructure. Only the largest organizations deploy these privately. Costs become significant for training and inference. Use cases must justify this level of investment.
Assess Customization and Fine-Tuning Capabilities
Your private LLM should accept custom training. Industry-specific terminology needs recognition. Fine-tuning on internal documents improves relevance. Generic models miss organizational context.
Check how easily you can update the model. New products and policies require knowledge updates. Retraining frequency affects operational costs. The process should be straightforward and documented.
Evaluate prompt engineering flexibility. Custom prompts guide model behavior effectively. Your team needs ability to refine instructions. This control ensures outputs match expectations.
Step 3: Establish Secure Connection Protocols
Security becomes paramount when you Connect Internal Database to Private LLM systems. Multiple layers of protection prevent unauthorized access. Every connection point needs careful configuration.
Design Network Architecture
Isolate the LLM environment from general network traffic. Create dedicated VLANs or subnets for AI infrastructure. The database and model should communicate through private channels. Public internet never touches these connections.
Implement firewall rules restricting traffic flow. Only allow necessary ports and protocols. The LLM needs database access but nothing else. Deny-by-default policies provide strongest protection.
Use VPN tunnels for remote administrative access. Never expose database ports to the internet. Encrypted connections protect credentials and data. Multi-factor authentication adds another security layer.
Configure Authentication Mechanisms
Implement certificate-based authentication where possible. Passwords alone prove vulnerable to attacks. Digital certificates provide stronger identity verification. Rotate certificates regularly following security policies.
Enable database-level authentication for the LLM user. The model authenticates before executing any queries. Invalid credentials immediately terminate connection attempts. Failed authentication triggers security alerts.
Integrate with existing identity management systems. Single sign-on simplifies user access control. Centralized identity management improves security posture. Deactivating employee access affects all connected systems.
Set Up Encryption Standards
Encrypt all data in transit between systems. TLS 1.3 provides current best practices. Configure proper cipher suites for maximum security. Weak encryption defeats the purpose of private deployment.
Enable encryption at rest for database storage. Sensitive information needs protection even when inactive. Hardware security modules store encryption keys safely. This defense protects against physical theft.
Implement end-to-end encryption for user queries. Inputs should encrypt before leaving user devices. The LLM decrypts only after authentication. This prevents interception of sensitive questions.
Monitor and Log All Connections
Deploy comprehensive logging for connection events. Record every attempt to access the database. Timestamps, user IDs, and query details need capture. Logs feed into security information systems.
Set up real-time alerting for suspicious activity. Unusual query patterns might indicate compromise. Geographic access from unexpected locations raises flags. Automated responses can block threats immediately.
Conduct regular security audits of connection logs. Manual review catches automated systems might miss. Look for privilege escalation attempts. Compliance teams need these records readily available.
Step 4: Implement the Database-to-LLM Bridge
The technical integration requires careful implementation. Several architectural approaches exist for connecting systems. Your choice depends on specific requirements and constraints.
Build a Query Translation Layer
Create middleware that sits between the LLM and database. This layer translates natural language into SQL queries. The LLM generates intent, middleware creates safe queries. This separation improves security and maintainability.
Implement query validation before database execution. Check for potentially harmful operations. Prevent data deletion or unauthorized modifications. Only approved query types reach the actual database.
Add result formatting to make outputs human-readable. Raw database returns often need cleanup. The middleware transforms technical data into natural language. Users receive polished, understandable responses.
Choose Integration Architecture Patterns
The API gateway pattern provides centralized control. All requests flow through a single entry point. Rate limiting and authentication happen here. This architecture simplifies monitoring and security.
The direct connection pattern links LLM and database closely. Latency decreases without middleware overhead. Security relies heavily on proper configuration. Smaller deployments often use this simpler approach.
The microservices pattern distributes functionality across services. Different services handle authentication, translation, and execution. Scaling becomes more flexible with independent components. Complexity increases but so does robustness.
Handle Data Retrieval and Caching
Implement intelligent caching to reduce database load. Frequently asked questions don’t need repeated queries. Cache results for appropriate time periods. This improves response times significantly.
Configure cache invalidation strategies carefully. Stale data produces incorrect AI responses. Real-time requirements vary by use case. Balance freshness against performance needs.
Set query timeouts to prevent resource exhaustion. Complex queries sometimes run indefinitely. Timeouts free up resources for other requests. Users receive appropriate error messages instead of hanging.
Test Connection Reliability
Conduct load testing before production deployment. Simulate realistic user query volumes. Identify bottlenecks and resource limitations. Fix performance issues before users encounter them.
Test failure scenarios and recovery procedures. What happens when the database goes offline? Does the LLM handle connection errors gracefully? Proper error handling prevents user frustration.
Validate data accuracy across various query types. Compare LLM responses against manual database queries. Ensure the translation layer works correctly. Accuracy testing catches logic errors early.
Step 5: Deploy and Monitor the Integrated System
Successful deployment requires planning beyond technical setup. User adoption and ongoing maintenance determine long-term success. Monitoring ensures the system continues performing well.
Plan Your Rollout Strategy
Start with a limited pilot group of users. Choose technically savvy employees who provide good feedback. Identify issues before widespread deployment. Early adopters become internal champions.
Create comprehensive documentation for users. Explain how to phrase effective queries. Provide examples of useful questions. Clear guides increase adoption rates.
Develop training programs for different user groups. Technical teams need different guidance than business users. Customize training to specific use cases. Hands-on practice builds confidence.
Establish Usage Monitoring
Track query volumes and patterns over time. Growing usage indicates successful adoption. Declining activity might signal problems. These metrics inform resource allocation decisions.
Monitor response times and accuracy rates. Slow responses frustrate users quickly. Incorrect answers damage trust in the system. Performance metrics guide optimization efforts.
Collect user feedback systematically. Anonymous surveys reveal honest opinions. Direct feedback sessions provide detailed insights. This input drives continuous improvement.
Maintain Security Posture
Schedule regular security assessments of the integrated system. Penetration testing reveals vulnerabilities before attackers find them. Update security configurations based on findings. Threats evolve and defenses must adapt.
Keep all components updated with security patches. Vulnerabilities in databases or LLM software need immediate attention. Automated patch management reduces manual workload. Test updates in staging before production deployment.
Review access permissions quarterly. Employee roles change over time. Remove unnecessary access promptly. Audit logs help identify unused accounts.
Optimize Performance Continuously
Analyze slow queries to identify optimization opportunities. Database indexes might need adjustment. Query translation logic sometimes requires refinement. Performance tuning remains an ongoing process.
Scale resources based on actual usage patterns. Add compute power during peak hours. Reduce capacity overnight to control costs. Cloud deployments make dynamic scaling easier.
Refine the LLM’s understanding through feedback. User corrections teach the model better patterns. Regular fine-tuning improves accuracy. Your private model becomes increasingly valuable over time.
Advanced Considerations for Database-LLM Integration
Sophisticated implementations address nuanced requirements. These advanced topics enhance security and functionality. Consider these aspects as your system matures.
Handling Multi-Database Environments
Many organizations maintain multiple database systems. Legacy systems coexist with modern platforms. The LLM needs access across all sources. Unified query interfaces hide backend complexity.
Implement database abstraction layers carefully. Users shouldn’t need to know which database contains their data. The LLM determines appropriate sources automatically. This transparency improves user experience.
Manage data consistency across distributed systems. The same information might exist in multiple places. Ensure the LLM retrieves the authoritative version. Master data management principles apply here.
Implementing Data Masking and Anonymization
Protect personally identifiable information automatically. The LLM should mask sensitive fields in responses. Social security numbers and credit cards need protection. This happens regardless of user permissions.
Apply differential privacy techniques where appropriate. Add statistical noise to prevent individual identification. Aggregate queries maintain privacy better than detailed records. Compliance teams appreciate these protections.
Create synthetic data for testing and development. Never use production data in non-production environments. Synthetic datasets mimic real patterns safely. This practice prevents accidental exposure.
Managing Compliance Requirements
Different industries face varying regulatory requirements. Healthcare data demands HIPAA compliance. Financial information requires SOX controls. Your integration must satisfy applicable regulations.
Implement data retention policies in query responses. The LLM should respect deletion requirements. European GDPR grants users right to erasure. Your system must honor these requests.
Maintain audit trails for compliance reporting. Regulators expect detailed access records. Your logs should prove proper data handling. Compliance becomes easier with comprehensive documentation.
Scaling for Enterprise Deployment
Plan for growth from the beginning. User adoption often exceeds initial expectations. Infrastructure should scale without architectural changes. Cloud platforms simplify scaling significantly.
Implement geographic distribution for global organizations. Reduce latency by deploying regionally. Data sovereignty laws might require local storage. The architecture should support multiple regions.
Build redundancy into every component. Single points of failure create unacceptable risks. Database replication and LLM clustering provide resilience. Users expect constant availability.
Common Challenges and Solutions
Every implementation encounters obstacles. Learning from common issues saves time and frustration. These challenges affect most organizations attempting to Connect Internal Database to Private LLM systems.
Addressing Query Accuracy Issues
The LLM sometimes generates incorrect SQL queries. Schema complexity confuses the translation layer. Test queries against development databases first. Implement query review mechanisms for critical operations.
Provide schema documentation to the LLM. Clear descriptions help generate better queries. Examples of correct queries serve as templates. The model learns patterns from good examples.
Create guardrails preventing dangerous operations. Never allow DROP, DELETE, or TRUNCATE commands. Read-only access eliminates most risks. Critical modifications need human approval.
Resolving Performance Bottlenecks
Database queries sometimes run slower than expected. Missing indexes cause full table scans. Monitor query execution plans regularly. Add indexes where analysis shows benefits.
The LLM itself might respond slowly. Large models require substantial processing power. Consider smaller, faster models for simple queries. Reserve powerful models for complex reasoning.
Network latency affects response times significantly. Place the LLM close to the database physically. Reduce geographic distance between components. Every millisecond matters for user experience.
Overcoming User Adoption Barriers
Employees resist changing familiar workflows. Demonstrate clear value through concrete examples. Show how the LLM saves time on routine tasks. Success stories from peers encourage adoption.
Some users struggle with natural language queries. They revert to traditional SQL or reporting tools. Provide query templates and examples. Training builds confidence over time.
Trust issues arise from AI skepticism. Users doubt answer accuracy initially. Transparency about data sources builds confidence. Show the underlying query for verification.
Managing Cost Considerations
Private LLM infrastructure requires significant investment. Hardware costs exceed public API expenses initially. Calculate total cost of ownership carefully. Factor in data security value and compliance benefits.
Ongoing operational costs accumulate quickly. GPU resources consume substantial power. Cloud hosting bills grow with usage. Optimize resource allocation continuously.
Training and fine-tuning increase expenses. Custom models require computational resources. Budget for regular updates and improvements. The investment pays dividends through better performance.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long does connecting an internal database to a private LLM typically take?
Implementation timeframes vary based on complexity and resources. Simple deployments finish in weeks with dedicated teams. Complex enterprise integrations span several months. Proper planning accelerates the process significantly. Database preparation often takes longest initially. Your existing infrastructure maturity affects timeline greatly.
Can I connect multiple databases to one private LLM?
Yes, modern architectures support multiple database connections. The integration layer coordinates access across sources. Users query naturally without specifying databases. The LLM determines appropriate data sources automatically. This capability proves valuable for comprehensive analytics. Complexity increases with each additional database.
What happens if the database connection fails during operation?
Proper implementations include fallback mechanisms. Error messages inform users of connection issues. The system logs failures for administrator review. Cached responses might serve some queries temporarily. Users receive clear explanations rather than confusing errors. Automatic retry logic handles transient network problems.
Do I need a dedicated team to maintain the integration?
Maintenance requirements depend on deployment scale. Small implementations need part-time attention. Enterprise systems require dedicated staff. Database administrators gain new responsibilities. Machine learning engineers handle model updates. Security teams monitor for threats continuously.
How do I ensure the LLM doesn’t expose sensitive data?
Multiple security layers prevent data exposure. Access controls limit what the LLM can query. Response filtering masks sensitive information automatically. Audit logs track all data access. Regular security reviews identify vulnerabilities. Proper configuration remains critical for protection.
Can the private LLM work with legacy database systems?
Yes, integration works with most database platforms. SQL databases connect most easily. NoSQL and legacy systems require additional configuration. ODBC and JDBC drivers enable broad compatibility. Older systems might need modernization first. Data migration sometimes proves necessary.
What’s the minimum hardware required for a private LLM?
Requirements vary dramatically by model size. Small models run on single GPU servers. Enterprise deployments need multiple GPUs or TPUs. RAM requirements range from 32GB to hundreds. Storage needs depend on training data volume. Cloud providers offer flexible starting points.
How often should I update or retrain the private LLM?
Update frequency depends on your data change rate. Quarterly retraining suits most organizations. Rapidly evolving businesses need monthly updates. Monitor accuracy metrics to guide timing. New products or terminology require prompt updates. Automation simplifies the retraining process.
Read More:-How to Build a Custom AI Agent to Automate Your Customer Support
Conclusion

Organizations that Connect Internal Database to Private LLM systems unlock tremendous value. Your proprietary data becomes more accessible and useful. AI-powered insights arrive without compromising security. The five steps outlined here provide a clear implementation path.
Database preparation forms the essential foundation. Proper access controls and optimization prevent future problems. Choosing the right private LLM affects capabilities and costs. Secure connection protocols protect your most valuable assets.
The technical implementation requires careful attention. Query translation layers ensure safe database access. Monitoring and optimization maintain system performance. User adoption determines ultimate success or failure.
Advanced considerations enhance sophisticated deployments. Multi-database support and compliance features address enterprise needs. Common challenges have proven solutions through careful planning. Cost management requires balancing investment against value.
Starting small and expanding gradually reduces risk. Pilot programs validate approaches before full deployment. User feedback guides continuous improvement. Your system grows more valuable over time.
The effort to Connect Internal Database to Private LLM infrastructure pays significant dividends. Teams access information faster than ever before. Decision-making improves through AI-powered analysis. Competitive advantages emerge from better data utilization.
Security remains paramount throughout the process. Multiple protection layers prevent unauthorized access. Encryption and authentication safeguard sensitive information. Compliance requirements receive proper attention.
Performance optimization continues after initial deployment. Regular monitoring identifies improvement opportunities. Resource scaling matches actual usage patterns. The system evolves with organizational needs.
Begin your journey toward connected AI systems today. Assess your current database infrastructure thoroughly. Research appropriate private LLM solutions carefully. Plan security measures from the start.
The future belongs to organizations leveraging internal data effectively. Private LLMs provide the technology foundation. Secure database connections deliver the necessary information. Your competitive position strengthens through better AI integration.
Taking the first step matters most. Perfect implementations don’t exist initially. Learn and adapt as you progress. The rewards justify the investment and effort required.