Introduction
TL;DR Modern AI systems must process information the way humans do. People communicate through speaking, writing, and sharing images simultaneously. Building multimodal agents creates intelligent systems that understand and respond across all these channels seamlessly.
Traditional AI assistants handle one input type at a time. A chatbot processes text while a voice assistant handles audio. Image recognition systems work separately from language models. This fragmented approach limits user experience and application potential.
Multimodal agents break down these artificial barriers. Users can speak a question, upload a photo, and receive a text response. The system understands context across different media types. Natural interactions emerge when technology mirrors human communication patterns.
Table of Contents
Understanding Multimodal AI Systems
What Defines a Multimodal Agent
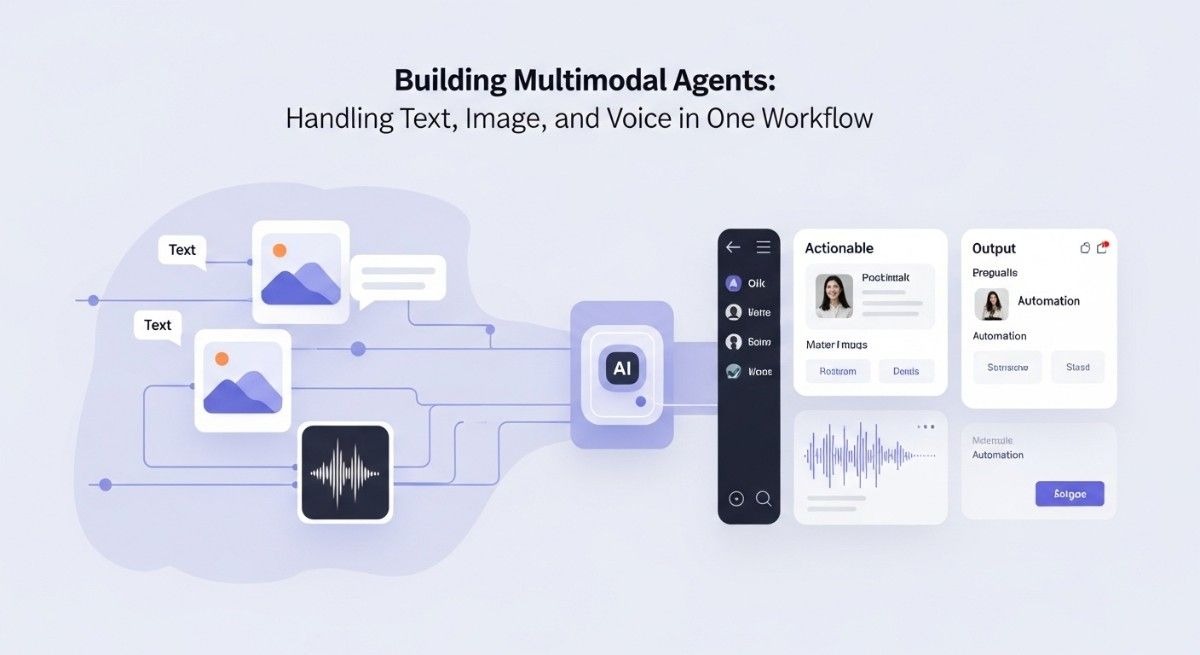
Multimodal agents process multiple input types within single interactions. Text, images, audio, and video flow through unified processing pipelines. The system maintains context across modality switches.
A user might photograph a broken appliance and ask “What’s wrong with this?” The agent analyzes the image while processing the spoken question. Diagnosis happens through combined understanding of visual and linguistic information.
Cross-modal reasoning distinguishes true multimodal systems from simple combinations. The agent draws connections between what it sees and what it hears. Image content informs language understanding and vice versa.
Memory systems track conversations across modality changes. Previous text exchanges influence current image analysis. Context accumulates regardless of input format.
Output generation matches user preferences and situational needs. Spoken questions might receive verbal answers. Complex visual queries could generate annotated images. Building multimodal agents requires flexible output capabilities.
The Evolution from Single-Modal to Multimodal
Early AI systems handled one data type exclusively. Computer vision algorithms processed images only. Natural language processors worked solely with text. Speech recognition operated in isolation.
Researchers began combining separate models through pipelines. Speech-to-text converters fed language models. Image captioning linked vision and language superficially. These approaches lacked true integration.
Transfer learning enabled models to share knowledge across domains. BERT representations helped image classification. Computer vision features improved text understanding. Shared representations bridged modalities.
Transformer architectures revolutionized multimodal processing. Attention mechanisms work across any data type. Self-attention discovers relationships between images and words. Cross-attention links audio to visual features.
Foundation models train on massive multimodal datasets simultaneously. CLIP learns vision-language connections from billions of image-text pairs. Flamingo handles interleaved visual and textual information. Unified training creates deeper cross-modal understanding.
Key Benefits of Multimodal Approaches
User experience improves dramatically with natural communication options. People choose the most convenient input method for each situation. Hands-free voice control while driving switches to text when quiet environments demand it.
Accessibility increases when multiple interaction modes exist. Visually impaired users rely on audio descriptions of images. Hearing-impaired individuals prefer text transcriptions of spoken content. Multimodal systems serve diverse user needs.
Accuracy improves through complementary information sources. Ambiguous text becomes clear with accompanying images. Noisy audio gets disambiguated through visual lip-reading. Multiple modalities provide redundancy and verification.
Application possibilities expand exponentially with multimodal capabilities. Medical diagnosis benefits from combining patient descriptions with medical imaging. E-commerce search improves when users upload product photos. Educational tools explain concepts through synchronized speech and diagrams.
Competitive advantage accrues to organizations deploying multimodal systems. User engagement metrics rise with richer interactions. Customer satisfaction scores improve through convenient communication. Building multimodal agents becomes a strategic imperative.
Core Technologies Behind Multimodal Agents
Vision Language Models and Architecture
Vision transformers process images as sequences of patches. Each patch becomes a token similar to words in sentences. Self-attention discovers spatial relationships across the image.
CLIP architecture aligns visual and textual representations. Images and descriptions map to shared embedding spaces. Similarity calculations enable zero-shot classification and retrieval.
Flamingo interleaves frozen vision encoders with language models. Perceiver resampler modules bridge modalities efficiently. Cross-attention layers fuse visual information into language processing.
GPT-4V extends large language models with vision capabilities. Image understanding happens natively within the language model. Users describe images or ask questions about visual content naturally.
DALL-E and Stable Diffusion generate images from text descriptions. Text encoders guide diffusion processes. Language becomes a control mechanism for visual creation.
LLaVA and MiniGPT-4 demonstrate efficient multimodal training. Visual encoders connect to language models through projection layers. Instruction tuning creates conversational image understanding.
Speech Recognition and Synthesis Integration
Automatic speech recognition converts audio waveforms to text. Wav2Vec 2.0 learns speech representations through self-supervision. Whisper achieves robust recognition across languages and accents.
Speech embeddings capture prosody, emotion, and speaker identity. Paralinguistic information enriches text transcriptions. Tone detection improves sentiment analysis accuracy.
Text-to-speech synthesis generates natural-sounding audio. Neural vocoders create high-fidelity waveforms. Voice cloning enables personalized audio experiences.
Speech translation systems understand audio in one language and speak another. Cascaded approaches combine recognition, translation, and synthesis. End-to-end models learn direct speech-to-speech mapping.
Voice activity detection segments continuous audio streams. Speaker diarization identifies who spoke when. These preprocessing steps enable natural conversations.
Real-time streaming capabilities allow instant responses. Low-latency models process audio incrementally. Users experience natural conversational flow without awkward pauses.
Natural Language Processing Foundations
Tokenization breaks text into processable units. Subword vocabularies handle multiple languages efficiently. Character-level models eliminate out-of-vocabulary problems.
Contextual embeddings capture word meaning based on surrounding text. BERT bidirectional encoding understands full sentence context. GPT causal modeling enables text generation.
Named entity recognition identifies people, places, and organizations. Relationship extraction discovers connections between entities. Knowledge graphs structure extracted information.
Sentiment analysis determines emotional tone in text. Aspect-based approaches identify opinions about specific topics. Fine-grained emotion classification detects nuanced feelings.
Question answering systems locate relevant information and formulate responses. Extractive QA pulls answers directly from documents. Generative QA synthesizes answers from multiple sources.
Dialogue management tracks conversation state and context. Intent classification determines user goals. Slot filling extracts specific information from requests. Building multimodal agents requires robust NLP foundations.
Design Patterns for Multimodal Workflows
Input Processing and Modality Fusion
Early fusion combines raw inputs before processing. Images and text concatenate into unified representations. Joint encoding captures cross-modal patterns from the start.
Late fusion processes each modality independently first. Separate encoders create modality-specific representations. Fusion layers combine these features for final predictions.
Hybrid fusion balances early and late approaches. Low-level features merge early for local interactions. High-level semantic features combine later for global understanding.
Attention-based fusion learns optimal combination strategies. Cross-modal attention discovers relevant connections dynamically. The model determines which modality matters most for each decision.
Gating mechanisms control information flow between modalities. Gates open or close based on input quality and relevance. Noisy audio might get downweighted while clear images dominate.
Temporal alignment synchronizes time-varying modalities. Audio words align with video frames showing speakers. Synchronized multimodal representations capture precise timing.
Context Management Across Modalities
Conversation history tracks all user interactions regardless of format. Previous images inform current text understanding. Earlier spoken questions provide context for new image queries.
Anaphora resolution connects pronouns to visual referents. “What color is it?” requires identifying “it” from previous images. Cross-modal coreference challenges traditional NLP approaches.
Memory architectures store long-term interaction patterns. User preferences learned from past conversations influence current responses. Personalization emerges from accumulated multimodal context.
Session management segments conversations into coherent units. Topic shifts trigger new session creation. Related interactions get grouped for contextual processing.
State tracking maintains structured representations of conversation progress. Dialogue states include accumulated information from all modalities. Slot values get filled through text, speech, or image analysis.
Context windowing limits computational costs for long conversations. Sliding windows retain recent interactions. Summarization compresses older context into compact representations.
Output Generation and Response Formatting
Text generation creates natural language responses. Temperature sampling controls creativity and randomness. Beam search finds high-probability response sequences.
Image generation produces visual outputs from multimodal context. Text descriptions guide image creation. Previous images inform style and content of new generations.
Speech synthesis converts text responses to audio. Voice characteristics match user preferences and contexts. Prosody conveys appropriate emotion and emphasis.
Multimodal responses combine output types strategically. Diagram generation accompanies textual explanations. Verbal descriptions enhance image presentations.
Format adaptation matches output to device capabilities. Mobile interfaces receive concise text and small images. Desktop users get detailed responses with high-resolution visuals.
Accessibility features ensure universal access to outputs. Screen readers vocalize text and describe images. Captions transcribe audio for hearing-impaired users. Building multimodal agents demands inclusive output design.
Technical Implementation Strategies
Choosing the Right Model Architecture
Task requirements determine optimal architecture choices. Simple applications might use pre-trained models directly. Complex domains benefit from fine-tuned specialized models.
Encoder-only architectures excel at understanding and classification. BERT-style models analyze text, images, or multimodal inputs. Embedding quality drives performance.
Decoder-only models generate text, images, or audio. GPT architectures scale effectively with data and compute. Autoregressive generation enables open-ended creation.
Encoder-decoder designs handle sequence-to-sequence tasks. Translation, summarization, and captioning fit this pattern. Separate encoding and generation optimize each process.
Unified transformer architectures process all modalities identically. Perceiver models handle arbitrary input types. Modality-agnostic designs simplify system complexity.
Mixture of experts routes inputs to specialized subnetworks. Different experts handle different modalities or tasks. Gating networks learn optimal routing strategies.
Data Pipeline Development
Data collection aggregates multimodal training examples. Web scraping gathers image-text pairs at scale. Crowdsourcing creates high-quality annotated datasets.
Preprocessing standardizes inputs across modalities. Images get resized and normalized. Audio undergoes noise reduction and normalization. Text receives tokenization and cleaning.
Augmentation expands training data diversity artificially. Image transformations include rotation, cropping, and color adjustment. Audio augmentation adds noise and pitch shifting. Paraphrasing diversifies text.
Quality filtering removes problematic training examples. Blurry images get discarded. Inaudible audio files get excluded. Offensive or biased text gets filtered.
Alignment verification ensures cross-modal correspondence. Image captions must accurately describe visual content. Audio transcriptions must match spoken words. Misaligned examples hurt model performance.
Batching strategies group similar examples for efficient training. Dynamic batching adjusts to varying input lengths. Modality-specific batching handles different data types separately.
Training and Fine-Tuning Approaches
Pre-training on large-scale multimodal datasets establishes foundational knowledge. Contrastive learning aligns modality representations. Masked prediction teaches within-modality understanding.
Transfer learning adapts pre-trained models to specific tasks. Feature extraction freezes base models and trains classification heads. Fine-tuning updates all parameters with domain data.
Multi-task learning trains single models on related tasks simultaneously. Shared representations benefit all tasks. Task-specific heads handle unique output requirements.
Instruction tuning teaches models to follow natural language directives. Examples demonstrate desired input-output behaviors. Zero-shot generalization emerges from diverse instruction following.
Reinforcement learning from human feedback refines model outputs. Human raters score response quality. Reward models guide further training toward preferred behaviors.
Continual learning prevents catastrophic forgetting. Rehearsal strategies retain previous knowledge while learning new tasks. Elastic weight consolidation protects important parameters. Building multimodal agents requires thoughtful training strategies.
Real-World Application Examples
Customer Service and Support Automation
Visual troubleshooting lets customers photograph problems. AI agents diagnose issues from images and descriptions. Step-by-step repair instructions include annotated photos and videos.
Voice-based navigation guides users through support processes. Hands-free interaction suits situations where typing proves difficult. Natural conversation feels more personal than form filling.
Product identification happens through images uploaded by customers. Visual search finds matching items in catalogs. Compatibility checks ensure correct replacement parts.
Sentiment analysis detects customer frustration in text and voice. Escalation protocols route angry customers to human agents. Empathetic responses acknowledge emotional states.
Knowledge base search combines text queries with visual examples. Users describe problems verbally while showing relevant screenshots. Multimodal retrieval finds more relevant solutions.
Chat history spans text messages, voice calls, and shared images. Agents access complete interaction context. Continuity improves even when customers switch communication channels.
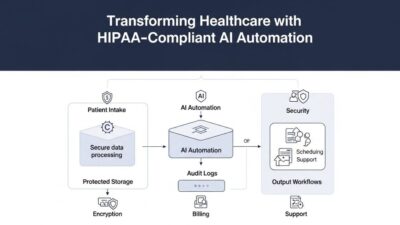
Healthcare Diagnostics and Patient Care
Medical imaging analysis combines radiological scans with patient histories. X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans get interpreted alongside symptoms. Differential diagnosis considers all available information.
Symptom checkers accept spoken descriptions and photos. Rashes get assessed visually while patients describe sensations. Preliminary diagnoses guide triage decisions.
Medication identification recognizes pills from photos. Patients photograph unfamiliar medications for identification. Safety warnings highlight potential interactions.
Remote patient monitoring analyzes sensor data, images, and self-reports. Wound healing gets tracked through sequential photographs. Voice journals supplement objective measurements.
Mental health assessments incorporate facial expressions and vocal patterns. Depression screening detects mood through multiple signals. Therapy chatbots offer multimodal emotional support.
Medical education platforms explain procedures through synchronized narration and video. Students ask questions about anatomical images. Interactive learning adapts to individual comprehension levels.
E-Commerce and Retail Innovation
Visual search revolutionizes product discovery. Shoppers photograph items they like and find similar products. Style matching considers overall aesthetic rather than exact duplicates.
Virtual try-on overlays clothing or makeup onto customer photos. Augmented reality shows furniture in home environments. Purchase confidence increases through visualization.
Voice shopping enables hands-free purchasing. Customers reorder groceries while cooking. Smart speakers handle routine purchases conversationally.
Product comparison synthesizes reviews, images, and specifications. Customers describe needs in natural language. AI recommends options with visual and textual explanations.
Size and fit prediction analyzes customer photos and measurements. Body type matching reduces returns from poor fit. Personalized recommendations improve satisfaction.
Customer reviews get analyzed across text, photos, and videos. Sentiment analysis identifies common praise and complaints. Visual content reveals actual product appearance. Building multimodal agents transforms retail experiences.
Education and Training Systems
Interactive tutoring adapts to student learning styles. Visual learners receive diagrams and videos. Auditory learners get spoken explanations. Reading-focused students receive text.
Homework help accepts photos of problem sets. Students ask questions about specific steps. Solutions include worked examples and conceptual explanations.
Language learning benefits from pronunciation feedback and visual context. Students practice speaking while viewing relevant images. Immersive scenarios simulate real conversations.
Accessibility accommodations serve diverse student needs. Dyslexic students receive audio versions of text. Visually impaired students get detailed image descriptions.
Assessment systems evaluate student responses across modalities. Essay writing, diagram labeling, and oral presentations get scored. Comprehensive evaluation captures varied competencies.
Collaborative learning platforms enable multimodal group interactions. Students share screens, speak, and chat simultaneously. Rich communication fosters deeper understanding.
Performance Optimization Techniques
Model Compression and Efficiency
Quantization reduces numerical precision of model weights. 8-bit integers replace 32-bit floats. Model size shrinks dramatically with minimal accuracy loss.
Pruning removes unnecessary neural network connections. Sparse models run faster and consume less memory. Structured pruning maintains hardware efficiency.
Knowledge distillation transfers large model capabilities to smaller ones. Student models learn from teacher predictions. Compact models achieve competitive performance.
Neural architecture search discovers efficient model designs. Automated exploration finds optimal accuracy-efficiency trade-offs. Hardware-aware search optimizes for specific deployment targets.
Early exit mechanisms stop processing when confidence reaches thresholds. Simple examples exit after few layers. Computational resources get allocated to difficult cases.
Caching stores frequent query results. Popular questions receive instant responses. Cache invalidation maintains freshness as underlying data changes.
Latency Reduction Strategies
Streaming inference processes inputs incrementally. Partial results get returned before complete input arrives. Users experience responsive interactions even with long inputs.
Speculative execution predicts likely next processing steps. Pre-computation happens before user input completes. Latency hides behind parallel processing.
Edge deployment moves computation closer to users. Local processing eliminates network round-trip delays. Privacy improves when data stays on-device.
Request batching amortizes overhead across multiple queries. Throughput increases though individual latency rises slightly. Batch size tuning balances competing objectives.
Asynchronous processing returns immediate acknowledgments. Long-running computations happen in background. Users stay engaged while waiting for results.
Load balancing distributes requests across multiple servers. Geographic routing minimizes network distances. Redundancy provides fault tolerance. Building multimodal agents requires performance optimization.
Scalability Considerations
Horizontal scaling adds more servers to handle increased load. Stateless request handling enables simple distribution. Load balancers route traffic efficiently.
Vertical scaling upgrades individual server capabilities. GPU acceleration speeds multimodal processing. Memory expansion supports larger models and batches.
Microservices architecture decomposes systems into independent components. Speech recognition, vision, and language services scale independently. Failure isolation contains outages.
Database sharding partitions data across multiple storage systems. User data gets distributed by region or ID range. Query performance remains consistent as data grows.
Content delivery networks cache static assets globally. Model weights and common responses get distributed widely. Bandwidth costs decrease while latency improves.
Auto-scaling adjusts resources based on demand patterns. Traffic spikes trigger automatic capacity increases. Idle resources get released to control costs.
Security and Privacy Considerations
Data Protection Across Modalities
Encryption protects data in transit and at rest. TLS secures network communications. Storage encryption prevents unauthorized access to databases.
Access controls limit who can view sensitive information. Role-based permissions enforce least privilege principles. Audit logs track all data access.
Data minimization collects only necessary information. Excessive data collection increases breach exposure. Privacy-preserving designs avoid storing sensitive data.
Anonymization removes personally identifiable information. Faces get blurred in images. Voices get masked in audio recordings. Text gets redacted.
Secure multiparty computation enables privacy-preserving collaboration. Multiple parties compute joint functions without revealing inputs. Encrypted data gets processed without decryption.
Differential privacy adds mathematical privacy guarantees. Statistical noise prevents individual record reconstruction. Aggregate insights get shared while protecting individuals.
Preventing Adversarial Attacks
Adversarial examples exploit model vulnerabilities. Carefully crafted inputs cause misclassifications. Adversarial training improves robustness.
Input validation rejects malformed or suspicious data. Schema validation ensures proper formatting. Content filtering blocks prohibited material.
Rate limiting prevents abuse through excessive requests. Per-user quotas prevent denial-of-service attacks. Throttling protects infrastructure resources.
Anomaly detection identifies unusual usage patterns. Behavioral analysis flags compromised accounts. Automated responses mitigate detected threats.
Model watermarking embeds signatures in outputs. Generated images contain invisible markers. Watermarks prove content provenance and deter misuse.
Red teaming proactively tests system security. Ethical hackers attempt to break defenses. Discovered vulnerabilities get patched before exploitation. Building multimodal agents demands robust security.
Compliance and Ethical Guidelines
GDPR compliance requires explicit consent for data collection. Right to deletion enables users to remove their data. Data portability allows export to competing services.
COPPA protects children’s online privacy. Age verification prevents underage data collection. Parental consent becomes mandatory for minors.
Accessibility standards ensure usability for disabled users. WCAG guidelines apply to multimodal interfaces. Alternative modalities accommodate various disabilities.
Bias testing evaluates fairness across demographic groups. Protected characteristics get monitored for disparate impact. Debiasing techniques mitigate discovered unfairness.
Content moderation prevents harmful outputs. Violence, hate speech, and misinformation get filtered. Human review handles edge cases.
Transparency reporting discloses system capabilities and limitations. Users understand when they interact with AI. Deception undermines trust and violates ethics.
Testing and Quality Assurance
Multimodal Testing Strategies
Unit testing validates individual component functionality. Vision encoders get tested with diverse images. Speech recognizers face various accents and noise levels.
Integration testing verifies cross-modal interactions. Image-text pairs confirm proper alignment. Voice-to-text pipelines undergo end-to-end validation.
Performance benchmarking establishes baseline metrics. Response latency gets measured across modalities. Throughput testing identifies bottlenecks.
Stress testing evaluates behavior under extreme conditions. Massive concurrent requests simulate traffic spikes. Degradation patterns inform capacity planning.
Edge case testing probes boundary conditions. Unusual input combinations reveal unexpected failures. Robustness improves through comprehensive coverage.
User acceptance testing involves real users in evaluation. Feedback identifies usability issues. Iterative refinement addresses discovered problems.
Quality Metrics and Evaluation
Accuracy metrics quantify correctness across tasks. Image classification measures top-k accuracy. Speech recognition tracks word error rates.
Fluency scores evaluate generated text quality. Perplexity quantifies language model confidence. Human raters assess naturalness.
Semantic similarity measures alignment between modalities. Image captions should accurately describe visual content. Audio transcriptions must match spoken words.
User satisfaction surveys capture subjective quality. Net promoter scores indicate recommendation likelihood. Usability ratings identify friction points.
Task completion rates measure functional success. Failed transactions highlight UX problems. Abandonment analysis reveals pain points.
A/B testing compares alternative designs experimentally. Statistical significance ensures reliable conclusions. Incremental improvements compound over iterations. Building multimodal agents benefits from rigorous testing.
Deployment and Monitoring
Production Infrastructure Setup
Container orchestration manages service deployment. Kubernetes automates scaling and failover. Docker images package application dependencies.
API gateways handle request routing and authentication. Rate limiting prevents abuse. Request transformation adapts protocols.
Message queues decouple components asynchronously. RabbitMQ and Kafka buffer traffic spikes. Reliability improves through persistent messaging.
Database replication ensures high availability. Read replicas distribute query loads. Automatic failover maintains uptime during outages.
CDN integration accelerates global delivery. Static assets get cached near users. Dynamic content benefits from edge computing.
Secrets management protects sensitive credentials. Vault systems encrypt API keys and passwords. Access controls limit exposure.
Observability and Logging
Distributed tracing tracks requests across services. Jaeger and Zipkin visualize complex flows. Performance bottlenecks become visible.
Metrics collection quantifies system health. Prometheus scrapes endpoint statistics. Grafana dashboards visualize trends.
Log aggregation centralizes diagnostic information. ELK stack indexes logs for searchability. Structured logging enables programmatic analysis.
Alerting systems notify teams of problems. Threshold violations trigger notifications. On-call rotations ensure rapid response.
Error tracking captures exceptions and stack traces. Sentry groups similar errors automatically. Prioritization focuses remediation efforts.
User session replay reconstructs problem scenarios. Screen recordings show exact user experiences. Reproduction accelerates debugging.
Continuous Improvement Processes
Feedback loops capture user input systematically. Thumbs up/down ratings identify good and bad responses. Detailed feedback explains user reactions.
Analytics reveal usage patterns and trends. Feature adoption metrics guide roadmap decisions. Drop-off analysis identifies improvement opportunities.
Model retraining incorporates new data continuously. Concept drift gets addressed through regular updates. Performance metrics validate improvements.
Experimentation platforms enable safe feature rollouts. Feature flags control exposure incrementally. Gradual rollout contains blast radius.
Incident post-mortems extract lessons from failures. Blameless culture encourages honest analysis. Process improvements prevent recurrence.
Competitive benchmarking tracks industry progress. Performance comparisons identify gaps. Innovation inspiration comes from adjacent domains. Building multimodal agents requires perpetual improvement.
Frequently Asked Questions
What programming languages work best for multimodal agents?
Python dominates AI development due to rich library ecosystems. PyTorch and TensorFlow provide deep learning frameworks. HuggingFace Transformers offers pre-trained multimodal models.
JavaScript enables browser-based multimodal applications. TensorFlow.js runs models client-side. Web APIs access cameras and microphones easily.
How much training data do multimodal models need?
Foundation models train on billions of examples. CLIP used 400 million image-text pairs. Organizations rarely need this scale for specific applications.
Fine-tuning requires much less data. Thousands of examples often suffice. Transfer learning leverages pre-trained model knowledge.
Can multimodal agents run on mobile devices?
Optimized models run efficiently on smartphones. Quantization and pruning reduce resource requirements. Edge deployment improves privacy and latency.
Cloud offloading handles computationally intensive tasks. Hybrid architectures balance local and remote processing. Network conditions determine optimal distribution.
What are common failure modes in multimodal systems?
Modality mismatch creates confusion. Unrelated images and text confuse models. Input validation prevents nonsensical combinations.
Cross-modal hallucination generates plausible but incorrect outputs. Vision-language models sometimes describe nonexistent image content. Confidence thresholds and verification reduce errors.
How do you handle multiple languages?
Multilingual pre-training enables language versatility. XLM-R and mT5 support 100+ languages. Translation models bridge language gaps.
Language detection identifies input languages automatically. Code-switching handles mixed-language inputs. Unicode support ensures proper character rendering.
What cloud platforms support multimodal AI?
AWS offers SageMaker for model training and deployment. Rekognition handles vision while Transcribe processes audio. Comprehend analyzes text.
Google Cloud provides Vertex AI platform. Vision AI, Speech-to-Text, and Natural Language form multimodal stacks. AutoML simplifies model development.
Azure Cognitive Services cover multiple modalities. Computer Vision, Speech Services, and Language Understanding integrate easily. Azure ML handles custom model development.
How much does multimodal AI cost?
Development costs vary dramatically by scope. Pre-trained models reduce expenses significantly. Custom training requires substantial compute resources.
Inference costs depend on usage volume. Pay-per-use pricing suits variable workloads. Reserved capacity reduces costs for predictable traffic.
What metrics indicate successful multimodal integration?
Task performance improves compared to single-modal baselines. Accuracy increases when combining complementary information. User engagement metrics rise with richer interactions.
Cross-modal retrieval effectiveness measures alignment quality. Images should match text descriptions semantically. Audio should align with visual content temporally.
Read More:-GitHub Copilot Extensions vs. Native AI IDEs: The Honest Truth
Conclusion

Building multimodal agents represents the future of human-computer interaction. Natural communication happens through whatever modality suits each moment. Technology finally mirrors human communication richness.
Technical foundations exist today for practical implementations. Pre-trained models eliminate need for massive datasets. Transfer learning accelerates development timelines dramatically.
Vision-language models understand images and text jointly. Speech processing adds conversational capabilities. Unified architectures handle all modalities seamlessly.
Design patterns guide effective workflow construction. Early and late fusion offer different trade-offs. Attention mechanisms learn optimal information combination.
Real-world applications demonstrate clear value. Customer service, healthcare, retail, and education benefit substantially. User experiences improve through multimodal flexibility.
Performance optimization makes deployment practical. Model compression reduces resource requirements. Latency reduction creates responsive interactions.
Security and privacy demand careful attention. Data protection spans all modalities. Adversarial robustness prevents exploitation.
Testing and monitoring ensure production quality. Comprehensive evaluation catches problems early. Continuous improvement sustains competitive advantage.
Implementation challenges exist but solutions are available. Cloud platforms provide managed infrastructure. Open-source tools democratize access.
Building multimodal agents requires interdisciplinary expertise. Computer vision, speech processing, and NLP knowledge combine. System design skills integrate components effectively.
The technology maturity curve accelerates rapidly. Foundation models improve monthly. Research breakthroughs become production features quickly.
Organizations investing now gain strategic advantages. First-mover benefits compound over time. User expectations shift toward multimodal interactions.
Accessibility improvements serve broader populations. Multiple modalities accommodate diverse abilities. Inclusive design benefits everyone.
Economic returns justify development investments. Automation reduces operational costs. Enhanced experiences drive revenue growth.
Building multimodal agents democratizes AI capabilities. Small teams build sophisticated applications. Pre-trained models level playing fields.
The path forward requires experimentation and learning. Start with focused use cases. Expand as expertise develops organically.
Ethical considerations must guide development. Bias testing ensures fairness. Transparency builds user trust sustainably.
Building multimodal agents transforms digital experiences fundamentally. Human-like communication becomes reality. The future of AI is decidedly multimodal.