Introduction
TL;DR Voice assistants have become household staples in just a few years. Millions of people talk to Alexa, Siri, or Google Assistant daily. The quality of these interactions depends entirely on AI listening behavior in voice assistants. Poor listening creates frustration and abandoned commands. Exceptional listening feels almost magical.
Most users don’t understand what happens behind the scenes. They just know when their voice assistant “gets it” or completely misses the point. The difference comes down to how sophisticated the listening mechanisms function. This guide reveals why AI listening behavior in voice assistants determines success or failure in voice user experience.
Table of Contents
The Foundation of Voice User Experience
Voice UX represents a fundamental shift from visual interfaces. Users can’t see menus or buttons. They rely entirely on spoken interaction. The assistant must understand commands accurately the first time. Second attempts break the flow and damage trust.
Speech recognition forms the first layer of voice interaction. Microphones capture audio. Algorithms convert sound waves into text. This transcription must handle accents, background noise, and speech variations. Errors at this stage doom the entire interaction.
Natural language understanding comes next. The system analyzes transcribed text for meaning. It identifies intent behind the words. A request for “weather” could mean current conditions or a forecast. Context determines the correct interpretation.
How Voice Differs From Text-Based Interaction
Speaking feels more natural than typing for most people. Conversations flow at 150-200 words per minute. Typing averages only 40 words per minute. Speed advantages make voice attractive for hands-free scenarios.
Users phrase voice commands differently than text queries. They speak in complete sentences rather than keyword strings. “What’s the weather like today in Boston?” replaces “Boston weather.” AI listening behavior in voice assistants must handle conversational language patterns.
Errors carry higher costs in voice interfaces. Visual interfaces let users scan options and self-correct. Voice provides no visual feedback. Users must listen carefully to responses. Mistakes force repetition of the entire interaction.
Immediacy expectations differ dramatically. People expect instant voice responses. Delays of even two seconds feel awkward. The conversation rhythm breaks. Users wonder if the system heard them at all.
Critical Components of Voice UX Success
Response accuracy determines user satisfaction more than any other factor. The assistant must understand what users actually want. Misinterpretation wastes time and creates frustration. High accuracy builds confidence and encourages continued use.
Conversation flow matters enormously in voice interactions. Natural pauses feel comfortable. Awkward silences create confusion. The assistant should respond at appropriate intervals. Timing affects whether exchanges feel human-like or robotic.
Error recovery separates good voice UX from great experiences. Mistakes will happen despite best efforts. How the system handles confusion determines overall quality. Graceful error management keeps interactions productive.
Personalization enhances voice experiences significantly. The assistant should recognize individual users. It adapts to speech patterns and preferences over time. Customized responses feel more helpful and relevant.
Understanding AI Listening Behavior in Voice Assistants
AI listening behavior encompasses how virtual assistants process and interpret spoken input. The technology involves multiple sophisticated steps. Each component contributes to overall comprehension quality. Weaknesses at any stage compromise the entire system.
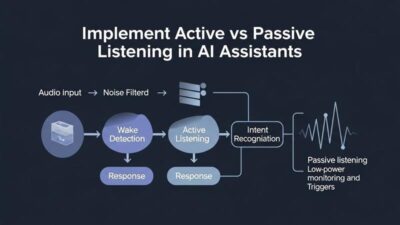
Wake word detection initiates the listening process. Devices constantly monitor for activation phrases. “Hey Siri” or “Alexa” triggers active listening mode. This monitoring must balance sensitivity and accuracy. False activations annoy users. Missed wake words frustrate them equally.
Audio processing cleans captured speech signals. Algorithms filter background noise. They enhance voice frequencies. The system separates speech from music, television, or other sounds. Quality processing dramatically improves recognition accuracy.
Speech Recognition Technology Explained
Acoustic models analyze sound patterns. They match audio to phonemes, the smallest sound units in language. These models train on thousands of hours of recorded speech. Diverse training data helps handle accents and speaking styles.
Language models predict likely word sequences. They use probability to choose between similar-sounding options. “Recognize speech” makes more sense than “wreck a nice beach” in most contexts. Statistical analysis selects the best interpretation.
Neural networks power modern speech recognition. Deep learning models process audio through multiple layers. Each layer extracts increasingly complex features. Output represents the most probable text transcription. Accuracy has improved dramatically with these approaches.
Continuous learning refines AI listening behavior in voice assistants over time. Systems analyze which interpretations led to successful outcomes. Failed interactions identify areas needing improvement. Models update regularly with new training examples.
Intent Recognition and Contextual Understanding
Users rarely state intentions explicitly. They ask “Is it cold out?” instead of “Check current temperature.” The assistant must infer the underlying goal. Intent recognition bridges the gap between words and meaning.
Entity extraction identifies key information within requests. Names, locations, dates, and numbers carry special significance. “Set alarm for 7 AM tomorrow” contains a time entity and date reference. Accurate extraction ensures correct action execution.
Context management tracks conversation history. Earlier exchanges inform interpretation of new input. “What about Thursday?” only makes sense with previous context. The system must remember relevant details throughout multi-turn dialogues.
Disambiguation strategies handle unclear requests. The assistant might ask clarifying questions. “Did you mean Boston, Massachusetts or Boston, England?” Multiple matches require user input. Smart disambiguation minimizes back-and-forth exchanges.
Technical Factors Affecting Listening Performance
Hardware quality significantly impacts AI listening behavior in voice assistants. Microphone arrays capture directional audio. Multiple microphones enable noise cancellation. Premium devices perform better in challenging acoustic environments. Budget hardware struggles with background sounds.
Processing power determines response speed. Complex neural networks demand substantial computation. Cloud processing offers unlimited resources but introduces latency. Edge computing reduces delays but limits model sophistication. The tradeoff affects user experience directly.
Network connectivity influences cloud-based assistants. Upload bandwidth affects audio transmission speed. Packet loss corrupts voice data. Poor connections cause timeouts and failed commands. Local processing avoids these issues but sacrifices capability.
Environmental Challenges and Solutions
Background noise represents the biggest listening challenge. Television audio, music, conversations, and ambient sounds interfere with speech recognition. Advanced algorithms must isolate the user’s voice. Beamforming focuses on sound from specific directions.
Echo and reverberation complicate audio processing. Hard surfaces reflect sound waves. The microphone captures both direct speech and reflections. Digital signal processing removes these artifacts. Room acoustics dramatically affect performance.
Distance from the device matters more than most realize. Optimal range sits between 3-10 feet for most assistants. Speaking too close causes audio clipping. Excessive distance reduces signal strength. Users must position themselves appropriately.
Multiple speakers create confusion. When two people talk simultaneously, AI listening behavior in voice assistants breaks down. The system struggles to separate overlapping voices. Most assistants handle only one speaker at a time.
Software Optimization Strategies
Language model tuning improves recognition accuracy. Developers customize models for specific domains. A cooking assistant learns recipe terminology. Smart home controllers understand device names. Specialized vocabulary boosts performance dramatically.
Confidence scoring helps identify uncertain interpretations. Low confidence triggers confirmation requests. “Did you say set alarm for 6 AM?” validates understanding before acting. This safety mechanism prevents costly errors.
Adaptive learning personalizes AI listening behavior. The system builds profiles of individual speech patterns. It learns preferred terminology and common requests. Performance improves through repeated interactions with each user.
Error analysis identifies systematic weaknesses. Developers examine failed interactions. Patterns reveal which accents, phrases, or contexts cause problems. Targeted improvements address the most common issues.
Impact on User Satisfaction and Adoption
User frustration builds quickly with poor listening quality. Repeated misunderstandings erode patience. People abandon voice assistants that don’t work reliably. First impressions matter enormously for adoption rates.
Trust develops through consistent accuracy. Users must believe the assistant understands them. Each successful interaction reinforces confidence. Reliability determines whether voice becomes a preferred interface.
Demographic factors influence satisfaction significantly. Older users often experience lower accuracy rates. Regional accents can confuse models trained primarily on standard dialects. Children’s voices present unique challenges. Inclusive AI listening behavior in voice assistants serves all user groups.
Usage Pattern Analysis
Successful interactions encourage expanded usage. People start with simple commands like timers or weather. Positive experiences lead to trying more complex tasks. Usage naturally grows when the assistant proves reliable.
Failed commands create avoidance behaviors. Users abandon features that didn’t work previously. They stick to proven commands rather than exploring capabilities. Poor listening permanently limits how people use assistants.
Context matters for command complexity. Users accept occasional errors during difficult scenarios. Perfect accuracy in quiet environments becomes the baseline expectation. Failure under ideal conditions damages credibility severely.
Emotional responses to voice interfaces run strong. Speaking feels personal compared to typing. Misunderstandings can feel like being ignored. The social nature of speech amplifies frustration from errors.
Competitive Differentiation Through Listening Quality
Market leaders distinguish themselves through superior AI listening behavior in voice assistants. Companies invest millions in improving accuracy. Small performance differences translate to major competitive advantages. Users notice when one assistant consistently outperforms another.
Brand loyalty develops around reliable voice experiences. Switching costs remain low in the voice assistant market. Users gravitate toward whichever option works best. Listening quality directly impacts market share.
Reviews and recommendations heavily emphasize understanding accuracy. Technology reviewers test assistants with challenging scenarios. Consumer reviews frequently mention whether the device “actually listens.” Word-of-mouth spreads based on listening performance.
Enterprise adoption depends on professional-grade reliability. Businesses can’t tolerate voice interfaces that require multiple attempts. Mission-critical applications demand near-perfect accuracy. Industrial and healthcare settings require specialized listening capabilities.
Real-World Applications and Industry Impact
Smart homes depend entirely on effective voice control. Users command lights, thermostats, locks, and appliances through speech. Poor AI listening behavior in voice assistants renders smart home systems frustrating. The promise of hands-free control falls flat when commands fail.
Automotive integration brings unique challenges. Road noise, music, and multiple passengers create difficult conditions. Drivers can’t look at screens for visual feedback. Voice must work flawlessly for safety reasons. Listening accuracy becomes a critical safety feature.
Healthcare applications require exceptional precision. Medical terminology includes complex words and similar-sounding drugs. Doctors dictate notes in noisy clinical environments. Errors could harm patients. Specialized listening models ensure accuracy in medical contexts.
Customer Service Automation
Call centers increasingly deploy voice AI. Automated systems handle routine inquiries. Customers expect human-level understanding. Poor listening drives callers to demand human agents. This defeats automation’s purpose and increases costs.
Authentication through voice biometrics adds security layers. Systems must recognize authorized users while rejecting imposters. The listening mechanism must balance security with usability. Overly strict matching frustrates legitimate users.
Multilingual support expands through voice interfaces. Customers speak their preferred language. The assistant must handle code-switching and accents. Global businesses need listening systems that work across languages and cultures.
Emotion detection enhances customer interactions. Voice tone reveals frustration, anger, or satisfaction. AI listening behavior in voice assistants that includes emotional analysis enables appropriate responses. Upset customers receive different treatment than happy ones.
Accessibility and Inclusion Benefits
Voice interfaces transform accessibility for people with disabilities. Blind users navigate smartphones through speech. Physical limitations preventing typing become irrelevant. Voice democratizes technology access when implemented well.
Elderly populations benefit from voice control. Vision and dexterity decline with age. Voice requires no fine motor skills. Seniors maintain independence through voice-controlled homes. Listening quality directly impacts their quality of life.
Literacy barriers disappear with voice interfaces. Reading ability doesn’t limit voice interaction. This opens technology to populations excluded by text-based systems. Education and information become more accessible globally.
Language learners practice through voice assistants. Pronunciation feedback helps improve speaking skills. The technology must handle non-native accents gracefully. Patient AI listening behavior in voice assistants encourages language practice.
Measuring and Optimizing Listening Performance
Word error rate quantifies recognition accuracy. This metric counts incorrect words in transcriptions. Lower percentages indicate better performance. Industry leaders achieve under 5% error rates in ideal conditions.
Intent classification accuracy measures understanding beyond transcription. The system might transcribe words correctly but misinterpret meaning. This metric reveals whether the assistant comprehends user goals. High intent accuracy correlates with user satisfaction.
Task completion rate tracks successful outcomes. Did the user accomplish their goal? This end-to-end metric captures overall effectiveness. Failed tasks indicate listening or execution problems somewhere in the chain.
User Experience Metrics
Response latency measures how quickly assistants reply. Users perceive delays above 300 milliseconds as sluggish. Competitive systems respond in under 200 milliseconds. Speed contributes significantly to naturalness perception.
Conversation abandonment rate reveals frustration levels. Users give up when interactions fail repeatedly. High abandonment indicates serious listening problems. This metric predicts long-term retention and engagement.
Repetition frequency shows how often users must rephrase commands. Multiple attempts signal comprehension failures. Well-tuned AI listening behavior in voice assistants minimizes repetition needs. Single-attempt success represents ideal performance.
User satisfaction scores aggregate subjective experiences. Surveys ask about ease of use and reliability. These ratings predict continued usage. Listening quality dominates satisfaction scores across all voice assistant studies.
Testing and Quality Assurance Methods
Synthetic testing generates thousands of test scenarios. Automated systems speak diverse commands. Performance gets measured across accents, volumes, and phrasings. This catches regressions before users encounter them.
Real-world beta testing validates laboratory findings. Actual users interact in their environments. Unexpected issues emerge that controlled testing missed. Beta feedback refines AI listening behavior before wide release.
Accent diversity testing ensures inclusive performance. Models must work for users regardless of geographic origin. Testing includes speakers from every major dialect region. Balanced accuracy across accents prevents discrimination.
Stress testing pushes systems to failure points. Extreme noise levels, multiple speakers, and unusual requests reveal breaking points. Understanding limitations guides appropriate use cases and user expectations.
Privacy and Security Considerations
Always-on microphones raise privacy concerns. Devices listen constantly for wake words. Users worry about unintended recording. Transparent data practices build trust. Companies must clearly communicate listening behavior.
Local processing protects sensitive information. Audio never leaves the device. Privacy improves but capability often decreases. The tradeoff between privacy and functionality requires user choice.
Data retention policies affect user comfort. Temporary storage enables learning and improvement. Permanent recording feels invasive. Clear deletion options give users control. Regulations increasingly mandate data minimization.
Balancing Functionality and Privacy
Voice profiling enables personalization. The system learns individual speech patterns. This improves accuracy but requires storing voice data. Users must consent to this data collection. Opt-in approaches respect privacy while enabling better experiences.
Third-party integrations multiply privacy considerations. Skills and actions often access external services. AI listening behavior in voice assistants must protect data across the entire ecosystem. Security vulnerabilities anywhere endanger user information.
Encryption protects transmitted audio. End-to-end encryption prevents interception during cloud processing. At-rest encryption secures stored recordings. Strong cryptography maintains confidentiality throughout the data lifecycle.
Anonymous analytics inform improvements without identifying users. Aggregate statistics reveal system-wide patterns. Individual privacy stays protected. This approach balances development needs with user rights.
Future Directions in Voice Assistant Technology
Multimodal interaction combines voice with visual feedback. Screens show relevant information while users speak. This hybrid approach leverages strengths of both modalities. Complex information displays visually while simple commands use voice.
Emotion-aware responses adapt to user feelings. The system detects stress, excitement, or confusion. Replies adjust appropriately to emotional states. Empathetic AI listening behavior in voice assistants creates more human interactions.
Proactive assistance anticipates needs before users ask. Context awareness triggers helpful suggestions. The assistant notices patterns and offers relevant information. This transforms voice interfaces from reactive to genuinely intelligent.
Emerging Technologies
Edge AI enables sophisticated processing locally. Powerful chips in devices run complex models. Cloud dependency decreases. Privacy improves while response speed increases. The tradeoff between local and cloud processing continues evolving.
Federated learning trains models without centralizing data. Devices contribute to collective improvement while keeping voice samples private. This technology resolves the tension between learning and privacy. Models improve from millions of interactions without storing personal recordings.
Neural speech synthesis creates natural-sounding responses. Generated voices match human prosody and emotion. Conversations feel more natural. High-quality synthesis complements improved AI listening behavior in voice assistants for complete experiences.
Cross-language understanding eliminates translation needs. The assistant comprehends multiple languages simultaneously. Users switch languages mid-conversation. Global communication barriers fall as this technology matures.
Best Practices for Implementing Voice Interfaces
Start with clear use case definition. Not every application benefits from voice control. Identify scenarios where hands-free or eyes-free interaction provides value. Force-fitting voice where it doesn’t belong frustrates users.
Design for conversation rather than commands. Natural language feels more comfortable than rigid syntax. Allow multiple ways to express the same intent. Flexible AI listening behavior in voice assistants accommodates individual speaking styles.
Provide clear feedback about system state. Users need to know when the device is listening. Audio or visual cues confirm active attention. Uncertainty about whether the system heard them creates anxiety.
Development Guidelines
Test with diverse users early and often. Developers’ voices and speech patterns aren’t representative. Real user testing reveals accent and terminology issues. Iterate based on actual performance data from target audiences.
Build robust error handling from the start. Plan for misunderstandings and unclear requests. Graceful degradation maintains usability despite imperfect AI listening behavior. Clear error messages help users recover quickly.
Optimize for the most common use cases first. The 80/20 rule applies strongly to voice interfaces. Perfect the frequent tasks before adding edge case features. Depth beats breadth for user satisfaction.
Document limitations honestly. Users appreciate knowing what the assistant can and cannot do. Setting accurate expectations prevents frustration. Transparency about capabilities builds trust even when functionality remains limited.
Continuous Improvement Strategies
Monitor usage analytics constantly. Track success rates for different command types. Identify patterns in failures. Data-driven optimization targets actual pain points rather than hypothetical issues.
Collect user feedback systematically. In-app surveys capture satisfaction data. Support tickets reveal recurring problems. Community forums provide unfiltered user perspectives. Multiple feedback channels paint complete pictures.
Update models regularly with new training data. Language evolves constantly. New products and features require vocabulary updates. Stale models gradually degrade in accuracy. Maintenance schedules prevent performance decay.
A/B test improvements before wide deployment. Compare new models against current production. Measure impact on key metrics. Roll out changes gradually. This careful approach prevents regression.
Frequently Asked Questions
What makes AI listening behavior in voice assistants different from regular speech recognition?
AI listening behavior encompasses much more than converting speech to text. The system interprets meaning, understands context, and infers intent. Regular speech recognition stops at transcription. Voice assistants analyze what users actually want to accomplish. They remember conversation history. They adapt to individual speaking patterns. This comprehensive approach enables natural interactions impossible with basic recognition.
How do voice assistants handle different accents and speaking styles?
Modern systems train on diverse speech samples from multiple regions. Acoustic models learn to recognize varied pronunciations. Language models accommodate different vocabulary choices. User-specific adaptation further improves accuracy. The system learns each person’s unique patterns. Performance varies by accent. Major dialects work well. Rare accents may experience lower accuracy. Companies continuously expand training data to improve global coverage.
Why does my voice assistant sometimes activate when I didn’t say the wake word?
Wake word detection balances sensitivity with specificity. False rejections frustrate users who do say the wake word. False acceptances annoy people when devices activate randomly. Similar-sounding phrases sometimes trigger activation. Background audio from television can contain wake word sounds. Manufacturers tune detection thresholds carefully. Some false positives remain unavoidable. Adjusting microphone sensitivity settings can reduce random activations.
How can I improve my voice assistant’s understanding of my commands?
Speak clearly at normal conversation volume. Avoid excessive distance from the device. Minimize background noise when possible. Use complete sentences rather than keywords. Be specific about what you want. Rephrase commands that fail consistently. The assistant learns from your corrections. Review privacy settings to enable personalized learning. Give the system time to adapt to your voice. Accuracy typically improves over several weeks of use.
Do voice assistants work equally well for children and elderly users?
Children’s voices present unique challenges. Higher pitches and different vocal tract lengths affect acoustic models. Many systems struggle with young children initially. Some assistants offer kid-specific modes. Elderly users often speak more slowly. Clarity sometimes decreases with age. Well-designed AI listening behavior in voice assistants accommodates these variations. Performance gaps have narrowed significantly. Inclusive design prioritizes serving all age groups equally.
What happens to my voice recordings after the assistant processes them?
Policies vary by company and device. Many systems store audio temporarily for quality improvement. Users can typically delete recordings through privacy settings. Some services offer automatic deletion after set periods. Local processing avoids cloud storage entirely. Review specific privacy policies for your device. Most companies now provide clear data management controls. Regulations increasingly mandate transparency about voice data handling.
How do smart speakers handle requests in noisy environments?
Multiple microphones enable directional listening. Beamforming focuses on sound from the user’s location. Noise cancellation filters background sounds. Adaptive algorithms adjust to changing conditions. Performance degrades in extremely loud environments. Optimal range and moderate noise produce best results. Speaking louder doesn’t necessarily help. Clear enunciation matters more than volume. Premium devices generally handle noise better than budget options.
Read More:-5 Steps to Build Voice Brand Identity for Voice AI
Conclusion

AI listening behavior in voice assistants fundamentally determines whether voice interfaces succeed or fail. Users expect natural conversations with high accuracy. Technology must handle diverse accents, noisy environments, and ambiguous requests. The companies that master listening quality will dominate the voice assistant market.
Investment in listening capabilities pays dividends across all applications. Smart homes become more reliable. Customer service automation actually helps people. Accessibility features genuinely empower users with disabilities. Every improvement in comprehension multiplies value throughout the ecosystem.
Privacy concerns must balance against functionality needs. Users want personalization but fear surveillance. Transparent policies and strong security build necessary trust. Local processing offers privacy advantages. Cloud systems provide superior capability. Giving users choice respects individual preferences.
Testing and optimization never end in voice technology. Language evolves. User expectations rise. Competitors advance their capabilities. Companies must continuously refine AI listening behavior in voice assistants. Regular updates maintain performance. Stagnant systems quickly become obsolete.
The future promises even more natural interactions. Emotional intelligence will improve. Proactive assistance will anticipate needs. Multimodal experiences will combine voice with other inputs. The distinction between human and AI conversation will blur further.
Developers and businesses must prioritize listening quality from day one. It affects every metric that matters. User satisfaction, task completion, retention, and recommendations all depend on comprehension accuracy. Skimping on listening capability guarantees poor outcomes.
Understanding why AI listening behavior matters empowers better design decisions. The technology involves complex acoustic processing, natural language understanding, and contextual awareness. Each component requires careful optimization. Weakness anywhere compromises the entire experience.
Voice represents the most natural interface humans have. Speaking requires no training or technical skill. Making this interface work reliably demands sophisticated AI listening behavior in voice assistants. The effort creates technology that feels magical. When voice assistants truly understand us, they transform how we interact with the digital world.