Introduction
TL;DR The way AI assistants listen to users has changed everything about digital interactions. Your virtual assistant might hear you, but is it really listening? The difference between active vs passive listening in AI determines whether you get generic responses or truly helpful assistance.
Most people don’t realize their AI tools operate on different listening modes. Some assistants just process words. Others understand context, emotions, and intent. This guide breaks down exactly what separates these two approaches and why it matters for your business.
Table of Contents
Understanding the Fundamentals of AI Listening Systems
AI listening isn’t the same as human hearing. Machines process language through complex algorithms and neural networks. The system takes your input and runs it through multiple layers of analysis. What happens next depends entirely on how developers programmed the listening capabilities.
Traditional AI systems followed simple command-response patterns. You said something specific. The machine returned a pre-programmed answer. Modern assistants have evolved far beyond this basic interaction model.
Natural language processing powers today’s conversational AI. The technology breaks down sentences into meaningful components. It identifies subjects, verbs, objects, and relationships between words. Machine learning models train on millions of conversations to improve accuracy.
The Evolution of AI Communication Models
Early chatbots could barely handle straightforward questions. They failed when users deviated from expected scripts. Developers recognized these limitations quickly. They started building systems that could handle variations in language.
Voice recognition technology improved dramatically over the past decade. Speech-to-text conversion became more accurate. AI could finally understand different accents, speech patterns, and pronunciations. This advancement opened doors for more sophisticated listening mechanisms.
Context awareness became the next frontier. Developers wanted AI that remembered previous exchanges. They built systems that could reference earlier parts of a conversation. This memory function transformed how assistants interpreted new information.
What Defines Passive Listening in AI Technology
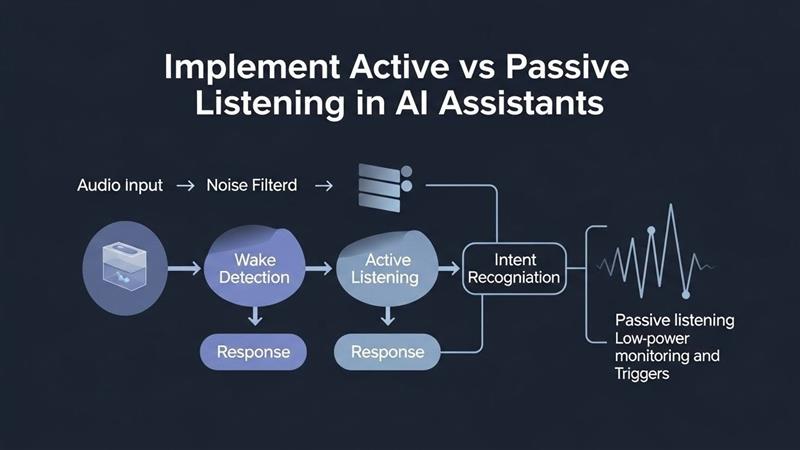
Passive listening in AI means the system receives input without deep analysis. The assistant hears your words but doesn’t engage with underlying meaning. It looks for keyword matches and triggers preset responses.
Think of passive listening like a basic search engine. You type a query. The system scans for matching terms. It returns results based on those exact words. There’s no interpretation of what you actually need.
Many customer service bots operate in passive mode. They wait for specific phrases to activate certain responses. Say “reset password” and they send password reset instructions. The interaction stays surface-level.
Characteristics of Passive AI Listening
Passive systems focus on word recognition rather than comprehension. They match your input against a database of known commands. The processing speed is fast because analysis remains shallow.
These systems struggle with ambiguity. They can’t handle multiple meanings or implied requests. Your phrasing must align closely with programmed variations. Deviation from expected input causes confusion or errors.
Response patterns stay predictable with passive listening. The AI delivers the same output for similar inputs. There’s no adaptation based on user history or context. Each interaction exists in isolation.
Passive listening works well for simple, repetitive tasks. Checking account balances, setting timers, or looking up basic information requires minimal interpretation. The straightforward nature of these requests suits passive processing.
Limitations That Impact User Experience
Users quickly hit walls with passive listening systems. The AI can’t understand nuanced questions. It misses sarcasm, emotion, and implied meaning. Frustration builds when the assistant keeps misunderstanding intent.
Context switching becomes problematic. You can’t reference something mentioned earlier in the conversation. The system treats each statement as independent. Building on previous topics requires starting over.
Problem-solving capabilities remain limited. Passive systems can’t break down complex issues. They can’t ask clarifying questions or suggest alternatives. The interaction stays transactional rather than conversational.
Personalization doesn’t exist in passive listening frameworks. The AI treats every user identically. It can’t adjust responses based on individual preferences or communication styles. This one-size-fits-all approach feels robotic and impersonal.
Active Listening Transforms AI Assistant Capabilities
Active vs passive listening in AI creates vastly different user experiences. Active listening means the system engages deeply with your input. It analyzes context, emotion, intent, and subtext. The AI doesn’t just hear words—it understands meaning.
Active listeners ask clarifying questions when something’s unclear. They confirm understanding before taking action. The conversation flows more naturally because the AI adapts to your communication style.
Context retention defines active listening systems. The AI remembers what you discussed five exchanges ago. It connects related topics across a conversation. This memory creates continuity that feels human-like.
Core Components of Active AI Listening
Natural language understanding forms the foundation. The system parses grammar, syntax, and semantics. It identifies relationships between concepts. Advanced models recognize idioms, metaphors, and cultural references.
Emotional intelligence separates good active listeners from great ones. The AI detects sentiment in your words. It recognizes frustration, excitement, confusion, or satisfaction. Responses adjust based on your emotional state.
Intent recognition goes beyond literal interpretation. The system infers what you’re trying to accomplish. You might ask “Is it cold outside?” but really want to know if you need a jacket. Active listeners pick up on these implied needs.
Contextual awareness pulls from multiple sources. The AI considers your conversation history. It factors in user preferences and past behaviors. It might even analyze the time of day or current events.
How Active Listening Improves Outcomes
Problem resolution happens faster with active listening. The AI grasps the root issue quickly. It doesn’t require you to explain things multiple times. Solutions become more targeted and effective.
User satisfaction scores climb significantly. People feel heard and understood. The interaction quality matches or exceeds human support in many cases. This positive experience builds trust in AI systems.
Complex tasks become manageable. Active listeners break down multi-step processes. They guide you through complicated procedures. The AI adapts explanations based on your technical knowledge level.
Proactive assistance emerges naturally. The system anticipates needs based on context. It might suggest related actions or offer relevant information. This helpfulness transforms AI from reactive to genuinely supportive.
Technical Implementation of Active vs Passive Listening in AI
Building active listening capabilities requires sophisticated architecture. Developers must integrate multiple AI technologies. Natural language processing handles initial text analysis. Machine learning models interpret meaning and context.
Training data quality determines listening effectiveness. Models learn from thousands or millions of conversation examples. Diverse datasets help AI understand different communication patterns. Poor training data results in biased or limited understanding.
Real-time processing presents technical challenges. The system must analyze input quickly while maintaining depth. Balancing speed and comprehension requires optimized algorithms. Cloud computing power enables these intensive calculations.
Architecture for Passive Listening Systems
Passive systems use simpler technology stacks. Rule-based processing handles most interactions. Developers create decision trees mapping inputs to outputs. Pattern matching identifies keywords and triggers responses.
Database lookups form the core function. User input gets matched against stored queries. The closest match determines which response gets delivered. This approach requires minimal computational resources.
Response templates populate most passive systems. Developers write fixed answers for common questions. Variables might personalize responses slightly. The fundamental structure stays identical across users.
Integration points remain straightforward. Passive listeners connect to basic APIs and databases. They don’t require complex neural networks or deep learning frameworks. Development and maintenance costs stay relatively low.
Building Active Listening Frameworks
Active systems demand advanced neural network architectures. Transformer models like BERT or GPT power understanding. These models process language bidirectionally. They grasp context from both preceding and following words.
Attention mechanisms help AI focus on relevant information. The system weighs different parts of input based on importance. This selective processing mimics how humans concentrate during conversations.
Memory management becomes critical. The AI must store and recall conversation history efficiently. Vector databases organize this information for quick retrieval. The system references past exchanges when interpreting new input.
Sentiment analysis modules detect emotional undertones. These components analyze word choice, punctuation, and phrasing patterns. The AI adjusts its tone and approach based on perceived user emotions.
Multi-turn dialogue management tracks conversation flow. The system maintains state across multiple exchanges. It knows what topics you’ve covered and what questions remain unanswered. This coherence creates natural conversations.
Real-World Applications and Use Cases
Customer service represents the most common application for active vs passive listening in AI. Companies deploy both types depending on needs and resources. Simple FAQs work fine with passive systems. Complex support issues demand active listening capabilities.
Healthcare assistants benefit enormously from active listening. Patients describe symptoms in varying ways. Active AI can interpret these descriptions accurately. It asks follow-up questions to narrow diagnoses. Passive systems might miss critical details.
Education platforms use active listening to personalize learning. The AI adapts to student comprehension levels. It identifies knowledge gaps through conversation. Custom explanations match individual learning styles.
Customer Support Transformations
Call centers increasingly rely on AI assistants. Passive systems handle routine inquiries about hours, locations, or basic policies. These interactions follow predictable patterns. Automated responses satisfy most customer needs.
Active listening AI tackles complicated problems. A customer might explain a billing issue with confusing details. The AI untangles the situation through strategic questioning. It validates understanding before proposing solutions.
First-call resolution rates improve with active systems. Customers don’t get transferred between departments. The AI comprehends the full problem scope. It either resolves issues directly or routes intelligently to specialists.
Customer satisfaction metrics reflect listening quality. Passive systems receive lower ratings for complex issues. Active listeners match or beat human agent satisfaction scores. Users appreciate not having to repeat information.
Healthcare and Mental Health Support
Medical symptom checkers need active listening capabilities. Patients rarely use clinical terminology. They describe sensations in everyday language. Active AI translates these descriptions into medical concepts.
Mental health chatbots provide therapeutic support. These systems must detect emotional nuances. They recognize when someone’s struggling even if words seem positive. Active listening enables appropriate interventions.
Medication management assistants track complex regimens. They understand when patients describe side effects. The AI asks targeted questions to assess severity. This detailed understanding keeps patients safe.
Appointment scheduling goes beyond picking dates. Active AI considers multiple factors—urgency, specialist availability, patient preferences. It negotiates conflicts and proposes optimal solutions.
Educational and Training Environments
Virtual tutors adapt to student needs through active listening. They identify misconceptions by analyzing answers. Explanations get tailored to specific confusion points. Learning accelerates when AI truly understands struggles.
Language learning apps employ active listening extensively. They catch pronunciation errors and grammar mistakes. The AI provides contextual corrections rather than generic rules. Conversations build naturally around student interests.
Corporate training systems assess comprehension through dialogue. Active AI identifies knowledge gaps during conversations. It reinforces weak areas without making learners feel inadequate. Training completion rates improve significantly.
Test preparation tools use active listening to simulate interviews. They analyze response quality and suggest improvements. The AI adapting questioning based on performance level. Students get personalized practice that targets weaknesses.
Measuring Effectiveness and Performance Metrics
Evaluating active vs passive listening in AI requires specific metrics. Response accuracy measures how often the AI understands intent correctly. This fundamental metric affects everything else.
Task completion rates show practical effectiveness. Can users accomplish their goals through AI interaction? Passive systems often fail at complex tasks. Active listeners complete multi-step processes successfully.
User satisfaction surveys provide subjective feedback. How natural did the conversation feel? Did users feel understood? These qualitative measures complement quantitative data.
Quantitative Performance Indicators
First-contact resolution tracks single-interaction success rates. Higher percentages indicate better comprehension and problem-solving. Active listeners typically score 30-40% higher than passive systems.
Average handling time shows efficiency gains. Active AI resolves issues faster by understanding quickly. Passive systems extend conversations through misunderstandings. Time savings translate to cost reductions.
Conversation depth metrics measure engagement quality. How many exchanges occur per session? Active listening extends conversations productively. Users willingly engage longer when AI understands them.
Error rates reveal comprehension accuracy. How often does the AI misinterpret requests? Passive systems show higher error rates with non-standard phrasing. Active listeners handle variation better.
Qualitative Assessment Methods
User sentiment analysis examines conversation tone. Does frustration increase or decrease during interactions? Active listening typically improves sentiment as conversations progress. Passive systems often generate increasing frustration.
Natural language review identifies common failure points. Where do users repeat themselves? When do they request human assistance? These patterns highlight listening gaps needing improvement.
A/B testing compares active and passive approaches. Companies run parallel systems with similar user groups. Direct comparison reveals performance differences. Results consistently favor active listening for complex scenarios.
Expert evaluation involves human reviewers assessing conversations. They rate understanding accuracy, response appropriateness, and overall quality. This qualitative feedback guides model improvements.
Challenges in Implementing Advanced Listening Systems
Building effective active listening requires significant resources. Development costs run higher than passive systems. Ongoing training and optimization demand continuous investment. Many organizations struggle with resource allocation.
Data privacy concerns complicate active listening. Systems must remember context while protecting sensitive information. Compliance with regulations like GDPR adds complexity. Balancing functionality and privacy requires careful architecture.
Bias in training data creates unfair outcomes. AI models learn from historical conversations. If training data contains biases, the system perpetuates them. Active listeners amplify these issues through deeper interpretation.
Technical Obstacles and Solutions
Computational requirements strain infrastructure. Active listening demands substantial processing power. Real-time analysis of context and emotion taxes systems. Cloud services help but increase operational costs.
Latency issues frustrate users. Delays between input and response break conversational flow. Optimizing model efficiency becomes crucial. Developers must balance depth of analysis with response speed.
Multi-language support multiplies complexity. Active listening requires understanding across languages. Cultural nuances vary widely. Building truly global systems demands extensive linguistic expertise.
Integration with existing systems poses challenges. Legacy infrastructure wasn’t designed for sophisticated AI. Organizations face difficult upgrade decisions. Hybrid approaches often bridge old and new technologies.
Ethical Considerations
Transparency about AI capabilities matters. Users should know they’re interacting with machines. Active listeners sound increasingly human. Clear disclosure prevents deception.
Manipulation risks increase with sophisticated listening. AI that understands emotions could exploit vulnerabilities. Ethical guidelines must govern implementation. Companies need clear policies on acceptable uses.
Dependency concerns emerge as AI improves. Users might prefer AI to human interaction. This shift could reduce human connection. Balancing convenience with social needs requires thoughtfulness.
Accountability becomes murky with active listeners. When AI makes mistakes interpreting complex input, who’s responsible? Clear liability frameworks protect both users and providers.
Future Trends in AI Listening Technology
The gap between active vs passive listening in AI will widen further. Emerging technologies enable even more sophisticated comprehension. Multimodal understanding combines voice, text, and visual input. AI will grasp meaning across multiple channels simultaneously.
Emotional intelligence will advance dramatically. Future systems will detect subtle mood shifts. They’ll recognize stress, excitement, or confusion from micro-indicators. Responses will adapt in real-time to emotional states.
Predictive listening represents the next frontier. AI won’t just understand current input. It will anticipate what users need next. Proactive assistance will feel magical rather than reactive.
Emerging Technologies
Quantum computing could revolutionize listening capabilities. Processing power increases exponentially. Complex analysis becomes instantaneous. Real-time deep understanding of long conversations becomes practical.
Brain-computer interfaces might bypass language entirely. Direct thought translation eliminates communication barriers. AI could understand intent without verbal expression. This technology remains experimental but shows promise.
Federated learning protects privacy while improving models. AI trains on distributed data without centralizing information. Active listening advances without compromising security. Users benefit from collective improvements privately.
Cross-lingual understanding will eliminate language barriers. AI will comprehend intent regardless of input language. Translation becomes semantic rather than literal. True global communication becomes possible.
Industry-Specific Developments
Legal AI will interpret complex regulations through active listening. Lawyers could describe cases naturally. The AI would identify relevant precedents and statutes. Legal research efficiency would increase dramatically.
Financial advisors will use AI with sophisticated listening. Clients express goals in personal terms. Active AI translates these into investment strategies. Personalized planning becomes accessible to everyone.
Creative industries will employ AI collaborators. Writers could brainstorm with active listeners. The AI understands creative direction and generates complementary ideas. Artistic collaboration between humans and machines will flourish.
Scientific research will accelerate through AI assistance. Researchers could discuss hypotheses naturally. Active listening AI would suggest experiments and analyze implications. Discovery processes would speed up significantly.
Best Practices for Choosing and Implementing AI Listening
Assess your specific needs before selecting technology. Simple, repetitive interactions work fine with passive listening. Complex problem-solving demands active capabilities. Mismatching technology to needs wastes resources.
Start with clear objectives and success metrics. What outcomes matter most? Faster resolution times? Higher satisfaction? Better first-contact resolution? Measurable goals guide implementation decisions.
Invest in quality training data. Your AI’s listening ability depends entirely on learning examples. Diverse, representative conversations train better models. Skimping on data quality guarantees poor performance.
Implementation Strategy
Begin with pilot programs. Test AI listening in controlled environments. Gather feedback from early users. Identify problems before full deployment. Iterative rollouts reduce risk significantly.
Provide human backup options. AI fails sometimes despite best efforts. Users need easy escalation paths. Hybrid approaches combining AI and human support work best initially.
Monitor performance continuously. Track metrics regularly. Identify degradation quickly. AI models drift over time without monitoring. Ongoing optimization maintains quality.
Gather user feedback systematically. Create easy channels for reporting issues. Users provide invaluable insights into AI performance. Their experiences should drive improvements.
Training and Maintenance
Update models regularly with new conversation data. Language evolves constantly. Slang changes, new terms emerge. Static models become outdated quickly. Continuous learning keeps AI current.
Test across diverse user groups. Different demographics communicate differently. Ensure AI understands various age groups, cultures, and education levels. Inclusive testing prevents bias.
Document AI limitations clearly. Users should know what the system can and cannot do. Setting appropriate expectations prevents frustration. Transparency builds trust.
Plan for scalability from the beginning. User bases grow. Conversation volumes increase. Infrastructure must handle expansion. Reactive scaling causes service disruptions.
Cost-Benefit Analysis of Active vs Passive Listening in AI
Passive systems cost significantly less to develop and maintain. Simple rule-based processing requires minimal infrastructure. Development timelines stay short. Organizations with tight budgets often choose passive approaches.
Active listening demands higher initial investment. Advanced models require expensive computational resources. Development takes longer. Specialized expertise costs more. The upfront commitment can seem daunting.
Long-term returns favor active listening for complex use cases. Higher first-contact resolution reduces support costs. Improved satisfaction increases customer retention. These benefits compound over time.
Financial Considerations
Development costs vary by complexity. Passive systems might cost $50,000 to $200,000 initially. Active listening projects start around $500,000 and can exceed several million. The difference reflects technical sophistication required.
Infrastructure expenses run higher for active systems. Cloud computing bills increase with processing demands. Organizations must budget for ongoing operational costs. These expenses remain significant but predictable.
Maintenance and updating require continuous investment. Active systems need regular model retraining. Data scientists and AI engineers command high salaries. Budget for permanent technical teams.
Cost per interaction drops dramatically with scale. Initial investment gets amortized across millions of conversations. Large organizations see rapid ROI. Small businesses struggle to justify advanced systems.
Return on Investment Metrics
Customer lifetime value increases with better experiences. Active listening creates satisfaction that drives loyalty. Retained customers generate more revenue over time. This impact often exceeds direct cost savings.
Operational efficiency gains materialize quickly. Fewer escalations to human agents reduce staffing needs. Active AI handles more complex issues independently. Labor cost reductions offset technology investments.
Revenue opportunities emerge from better understanding. Active listeners identify upsell opportunities naturally. They recognize when customers need additional products. Subtle recommendations feel helpful rather than pushy.
Brand reputation improves with quality AI interactions. Word-of-mouth recommendations increase. Social media sentiment becomes more positive. These intangible benefits have real financial impact.
Frequently Asked Questions
What makes active listening more effective than passive listening in AI systems?
Active listening analyzes context, emotion, and intent beyond just words. The AI remembers previous exchanges and adapts responses accordingly. This comprehensive understanding leads to accurate problem-solving. Passive systems match keywords without deeper comprehension. They miss nuances that determine actual user needs. The difference becomes obvious in complex interactions requiring multiple exchanges.
Can passive listening AI be upgraded to active listening capabilities?
Upgrading requires significant architectural changes. Simple rule-based systems can’t easily incorporate advanced natural language understanding. Organizations typically need to rebuild from the ground up. Some hybrid approaches add limited active features to passive frameworks. These compromises improve performance but don’t achieve full active listening. The decision depends on existing infrastructure and resource availability.
How does active vs passive listening in AI affect customer satisfaction scores?
Customer satisfaction correlates strongly with listening quality. Active systems score 25-40% higher in user satisfaction surveys. People feel understood and valued during interactions. Passive systems frustrate users with repetitive questions and misunderstandings. The gap widens for complex issues requiring contextual understanding. Simple transactions show smaller satisfaction differences.
What industries benefit most from active listening AI?
Healthcare sees dramatic improvements from active listening. Medical questions require understanding symptoms described in non-technical language. Financial services also benefit significantly. Customers explain goals in personal terms requiring interpretation. Education and mental health support demand emotional intelligence. Any industry dealing with complex, nuanced problems gains from active listening.
How much does it cost to implement active listening technology?
Implementation costs range from $500,000 to several million dollars. Factors include organization size, use case complexity, and integration requirements. Ongoing operational expenses add 15-30% annually. Passive systems cost 60-80% less initially. Organizations must weigh these expenses against potential benefits. ROI calculations should include both direct savings and indirect value improvements.
Does active listening AI work in multiple languages?
Advanced active listening systems support multiple languages. Training models for each language requires substantial effort. Performance varies by language due to training data availability. English generally works best due to extensive training examples. Other major languages perform well. Rare languages or dialects present challenges. Translation layers can help but may reduce accuracy.
How do you measure if your AI assistant truly listens actively?
Test with complex, multi-part questions requiring context. Active listeners remember earlier conversation elements. They ask clarifying questions when needed. Monitor first-contact resolution rates and conversation depth. User satisfaction surveys reveal whether people feel understood. Compare performance on ambiguous queries where intent isn’t explicit. Active systems interpret meaning while passive systems request clarification constantly.
Read More:-How to Detect Conversational UX Failure Modes Early
Conclusion

The distinction between active vs passive listening in AI fundamentally shapes user experience and outcomes. Passive systems serve well for simple, repetitive tasks where speed matters more than depth. Active listening transforms AI into genuine assistants capable of understanding nuance and context.
Organizations must carefully evaluate their specific needs and resources. Not every application requires sophisticated active listening. Budget constraints and use case complexity should drive decisions. Starting with clear objectives prevents costly mismatches between technology and requirements.
The future clearly favors active listening development. Technology advances make sophisticated comprehension increasingly accessible. Costs will decrease as models improve and become more efficient. Organizations investing in active listening today position themselves competitively for tomorrow.
User expectations continue rising. People want AI that truly understands them. They seek conversations that flow naturally without frustration. Active vs passive listening in AI represents more than technical choices. It determines whether your AI assistant helps or merely responds. The best systems make users forget they’re talking to machines.
Smart implementation balances capabilities with practical constraints. Hybrid approaches often work best initially. Organizations can start with passive systems and evolve toward active listening. Continuous improvement keeps pace with advancing technology and user expectations.
Success requires commitment beyond initial deployment. Regular monitoring, updating, and optimization maintain performance. User feedback drives meaningful improvements. The organizations that treat AI listening as an ongoing journey rather than a destination will reap the greatest rewards.
Understanding the differences empowers better decisions. Whether you’re building, buying, or using AI assistants, listening quality matters enormously. The gap between hearing words and understanding meaning separates mediocre tools from transformative technologies. Choose wisely based on your needs, and your users will thank you.